Immunology Antibodies 2
Anti-ATP6V0C Antibody (CAB16350)
- SKU:
- CAB16350
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Immunology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ATP6V0C Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16350 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
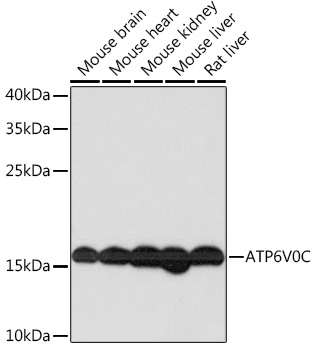
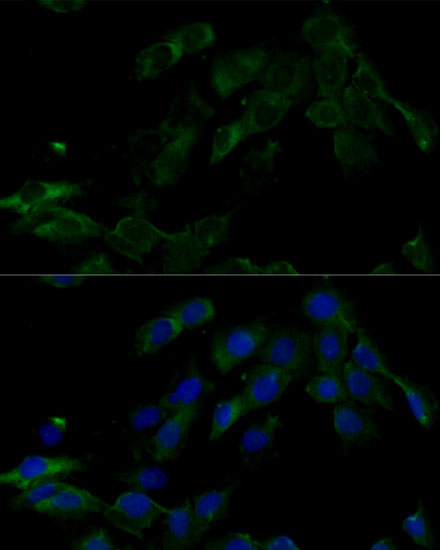
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 1-100 of human ATP6V0C (NP_001185498.1). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain, Mouse heart, Mouse kidney, Mouse liver, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 1-100 of human ATP6V0C (NP_001185498.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSES KSGP EYAS FFAV MGAS AAMV FSAL GAAY GTAK SGTG IAAM SVMR PEQI MKSI IPVV MAGI IAIY GLVV AVLI ANSL NDDI SLYK SFLQ LGAG LSVG |
| Gene ID: | 527 |
| Uniprot: | P27449 |
| Cellular Location: | Multi-pass membrane protein, Vacuole membrane |
| Calculated MW: | 15kDa |
| Observed MW: | 16kDa |
| Synonyms: | ATP6V0C, ATP6C, ATP6L, ATPL, VATL, VPPC, Vma3 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c", and d. This gene encodes the V0 subunit c. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants. Pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 6 and 17. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ATP6V0C: Proton-conducting pore forming subunit of the membrane integral V0 complex of vacuolar ATPase. V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying a variety of intracellular compartments in eukaryotic cells. Belongs to the V-ATPase proteolipid subunit family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Transporter, ion channel; Transporter, iron; Transporter Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16p13.3 Cellular Component: phagocytic vesicle membrane; focal adhesion; lysosomal membrane; integral to membrane; endosome membrane Molecular Function:protein binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism; hydrogen ion transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism Biological Process: interaction with host; proton transport; viral reproduction; cellular iron ion homeostasis; ATP hydrolysis coupled proton transport; insulin receptor signaling pathway; transferrin transport; transmembrane transport; positive regulation of Wnt receptor signaling pathway |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c", and d. This gene encodes the V0 subunit c. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants. Pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 6 and 17. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P27449 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 310832382 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 527 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_001185498.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P27449,Q6FH26, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P27449 |
| Molecular Weight: | 15,736 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | V-type proton ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 16kDa, V0 subunit c |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ATP6V0C |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ATPL; VATL; VPPC; Vma3; ATP6C; ATP6L |
| NCBI Protein Information: | V-type proton ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit; V-ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit; vacuolar H+ ATPase proton channel subunit; vacuolar proton pump 16 kDa proteolipid subunit; vacuolar ATP synthase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit; H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase, 16 kDa subunit |
| UniProt Protein Name: | V-type proton ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Vacuolar proton pump 16 kDa proteolipid subunit |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ATP6V0C |
| UniProt Entry Name: | VATL_HUMAN |