Signal Transduction Antibodies 2
Anti-ATP5J Antibody (CAB3751)
- SKU:
- CAB3751
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ATP5J Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB3751 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
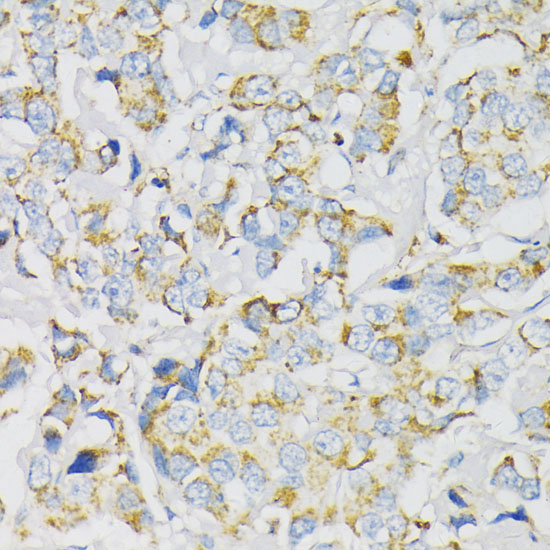
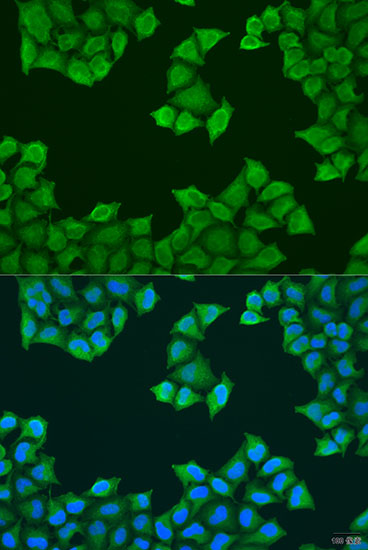
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-108 of human ATP5J (NP_001676.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
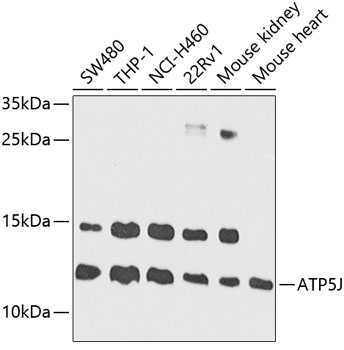
| Positive Samples: | SW480, THP-1, NCI-H460, 22Rv1, Mouse kidney, Mouse heart |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-108 of human ATP5J (NP_001676.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MILQ RLFR FSSV IRSA VSVH LRRN IGVT AVAF NKEL DPIQ KLFV DKIR EYKS KRQT SGGP VDAS SEYQ QELE RELF KLKQ MFGN ADMN TFPT FKFE DPKF EVIE KPQA |
| Gene ID: | 522 |
| Uniprot: | P18859 |
| Cellular Location: | Mitochondrion, Mitochondrion inner membrane |
| Calculated MW: | 12kDa/13kDa |
| Observed MW: | 13kDa |
| Synonyms: | ATP5J, ATP5, ATP5A, ATPM, CF6, F6 |
| Background: | Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. It is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, which comprises the proton channel. The F1 complex consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled in a ratio of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The Fo complex has nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). This gene encodes the F6 subunit of the Fo complex. The F6 subunit is required for F1 and Fo interactions. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. This gene has 1 or more pseudogenes. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ATP5J: Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain and the peripheric stalk, which acts as a stator to hold the catalytic alpha(3)beta(3) subcomplex and subunit a/ATP6 static relative to the rotary elements. Also involved in the restoration of oligomycin-sensitive ATPase activity to depleted F1-F0 complexes. Belongs to the eukaryotic ATPase subunit F6 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.6.3.14; Energy Metabolism - oxidative phosphorylation; Mitochondrial Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 21q21.1 Cellular Component: mitochondrion; mitochondrial inner membrane; mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex Molecular Function:transporter activity; ATPase activity; transmembrane transporter activity; hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity Biological Process: cellular metabolic process; substantia nigra development; mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport |
| NCBI Summary: | Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. It is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, which comprises the proton channel. The F1 complex consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled in a ratio of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The Fo complex has nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). This gene encodes the F6 subunit of the Fo complex. The F6 subunit is required for F1 and Fo interactions. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. This gene has 1 or more pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016] |
| UniProt Code: | P18859 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 114688 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 522 |
| NCBI Accession: | P18859.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P18859 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ATP synthase peripheral stalk subunit F6 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ATP5PF |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | F6; CF6; ATP5; ATPM; ATP5A; ATP5J |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Protein Name: | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial |
| Protein Family: | ATP synthase-coupling factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ATP5J |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ATP5J_HUMAN |
View AllClose