Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 4
Anti-ASXL1 Antibody (CAB9890)
- SKU:
- CAB9890
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ASXL1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9890 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
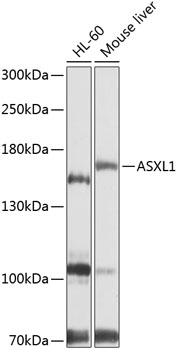
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 70-250 of human ASXL1 (NP_056153.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | HL-60, Mouse liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 70-250 of human ASXL1 (NP_056153.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LFYK LPGR ISLF TLKK DALQ WSRH PATV EGEE PEDT ADVE SCGS NEAS TVSG ENDV SLDE TSSN ASCS TESQ SRPL SNPR DSYR ASSQ ANKQ KKKT GVML PRVV LTPL KVNG AHVE SASG FSGC HADG ESGS PSSS SSGS LALG SAAI RGQA EVTQ DPAP LLRG FRKP ATGQ MKRN RGEE I |
| Gene ID: | 171023 |
| Uniprot: | Q8IXJ9 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 53kDa/165kDa |
| Observed MW: | 165kDa |
| Synonyms: | ASXL1, BOPS, MDS |
| Background: | This gene is similar to the Drosophila additional sex combs gene, which encodes a chromatin-binding protein required for normal determination of segment identity in the developing embryo. The protein is a member of the Polycomb group of proteins, which are necessary for the maintenance of stable repression of homeotic and other loci. The protein is thought to disrupt chromatin in localized areas, enhancing transcription of certain genes while repressing the transcription of other genes. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a ligand-dependent co-activator for retinoic acid receptor in cooperation with nuclear receptor coactivator 1. Mutations in this gene are associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ASXL1: Probable Polycomb group (PcG) protein involved in transcriptional regulation mediated by ligand-bound nuclear hormone receptors, such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG). Acts as coactivator of RARA and RXRA through association with NCOA1. Acts as corepressor through recruitment of KDM1A and CBX5 to target genes in a cell-type specific manner; the function seems to involve differential recruitment of methylated histone H3 to respective promoters. Acts as corepressor for PPARG and suppresses its adipocyte differentiation-inducing activity. Non-catalytic component of the PR-DUB complex, a complex that specifically mediates deubiquitination of histone H2A monoubiquitinated at 'Lys-119' (H2AK119ub1). Defects in ASXL1 are the cause of Bohring-Opitz syndrome (BOPS). A syndrome characterized by severe intrauterine growth retardation, poor feeding, profound mental retardation, trigonocephaly, prominent metopic suture, exophthalmos, nevus flammeus of the face, upslanting palpebral fissures, hirsutism, and flexion of the elbows and wrists with deviation of the wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints. Defects in ASXL1 are a cause of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). A heterogeneous group of closely related clonal hematopoietic disorders. All are characterized by a hypercellular or hypocellular bone marrow with impaired morphology and maturation, dysplasia of the myeloid, megakaryocytic and/or erythroid lineages, and peripheral blood cytopenias resulting from ineffective blood cell production. Included diseases are: refractory anemia (RA), refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts (RARS), refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB), refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia and ringed sideroblasts (RCMD-RS); chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease. MDS is considered a premalignant condition in a subgroup of patients that often progresses to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Belongs to the Asx family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Nuclear receptor co-regulator; Transcription regulation Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 20q11 Cellular Component: nuclear chromatin Molecular Function:peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding; protein binding; retinoic acid receptor binding; transcription coactivator activity; transcription corepressor activity Biological Process: negative regulation of fat cell differentiation; negative regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to retinoic acid Disease: Bohring-opitz Syndrome; Myelodysplastic Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is similar to the Drosophila additional sex combs gene, which encodes a chromatin-binding protein required for normal determination of segment identity in the developing embryo. The protein is a member of the Polycomb group of proteins, which are necessary for the maintenance of stable repression of homeotic and other loci. The protein is thought to disrupt chromatin in localized areas, enhancing transcription of certain genes while repressing the transcription of other genes. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a ligand-dependent co-activator for retinoic acid receptor in cooperation with nuclear receptor coactivator 1. Mutations in this gene are associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q8IXJ9 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 317373477 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 171023 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q8IXJ9.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q8IXJ9,Q5JWS9, Q8IYY7, Q9H466, Q9NQF8, Q9UFJ0, Q9UFP8 Q9Y2I4, B2RP59, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q8IXJ9 |
| Molecular Weight: | 53,374 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Putative Polycomb group protein ASXL1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | additional sex combs like 1, transcriptional regulator |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ASXL1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MDS; BOPS |
| NCBI Protein Information: | putative Polycomb group protein ASXL1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Putative Polycomb group protein ASXL1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Additional sex combs-like protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Putative Polycomb group protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ASXL1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ASXL1_HUMAN |