Metabolism Antibodies 1
Anti-ApoE Antibody (CAB12400)
- SKU:
- CAB12400
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ApoE Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB12400 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
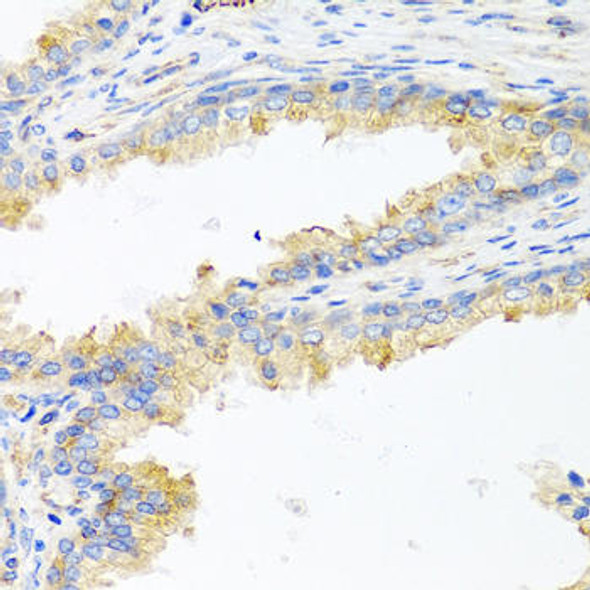
| Application: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 200-300 of human ApoE (NP_000032.1). |
| Application: | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | IHC 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | LO2, A-549, SKOV3, 293T, Mouse brain, Mouse liver, Rat liver, Rat ovary |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 200-300 of human ApoE (NP_000032.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | GPLV EQGR VRAA TVGS LAGQ PLQE RAQA WGER LRAR MEEM GSRT RDRL DEVK EQVA EVRA KLEE QAQQ IRLQ AEAF QARL KSWF EPLV EDMQ RQWA GLVE K |
| Gene ID: | 348 |
| Uniprot: | P02649 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted |
| Calculated MW: | 36kDa |
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |
| Synonyms: | APOE, AD2, APO-E, ApoE4, LDLCQ5, LPG, ApoE |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a major apoprotein of the chylomicron. It binds to a specific liver and peripheral cell receptor, and is essential for the normal catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein constituents. This gene maps to chromosome 19 in a cluster with the related apolipoprotein C1 and C2 genes. Mutations in this gene result in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, or type III hyperlipoproteinemia (HLP III), in which increased plasma cholesterol and triglycerides are the consequence of impaired clearance of chylomicron and VLDL remnants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Mediates the binding, internalization, and catabolism of lipoprotein particles. It can serve as a ligand for the LDL (apo B/E) receptor and for the specific apo-E receptor (chylomicron remnant) of hepatic tissues. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Subcellular location: Secreted. Tissue specificity: Occurs in all lipoprotein fractions in plasma. It constitutes 10-20% of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and 1-2% of high density lipoproteins (HDL). APOE is produced in most organs. Significant quantities are produced in liver, brain, spleen, lung, adrenal, ovary, kidney and muscle. Ref.18 Post-translational modification: Synthesized with the sialic acid attached by O-glycosidic linkage and is subsequently desialylated in plasma. O-glycosylated with core 1 or possibly core 8 glycans. Thr-307 is a minor glycosylation site compared to Ser-308. Ref.19Glycated in plasma VLDL of normal subjects, and of hyperglycemic diabetic patients at a higher level (2-3 fold).Phosphorylation sites are present in the extracelllular medium. Polymorphism: Three common APOE alleles have been identified: APOE*2, APOE*3, and APOE*4. The corresponding three major isoforms, E2, E3, and E4, are recognized according to their relative position after isoelectric focusing. Different mutations causing the same migration pattern after isoelectric focusing define different isoform subtypes. The most common isoform is E3 and is present in 40-90% of the population. Common APOE variants influence lipoprotein metabolism in healthy individuals. Involvement in Disease: Defects in APOE are a cause of hyperlipoproteinemia type 3 (HLPP3) [ MIM:107741]; also known as familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Individuals with HLPP3 are clinically characterized by xanthomas, yellowish lipid deposits in the palmar crease, or less specific on tendons and on elbows. The disorder rarely manifests before the third decade in men. In women, it is usually expressed only after the menopause. The vast majority of the patients are homozygous for APOE*2 alleles. More severe cases of HLPP3 have also been observed in individuals heterozygous for rare APOE variants. The influence of APOE on lipid levels is often suggested to have major implications for the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). Individuals carrying the common APOE*4 variant are at higher risk of CAD. Ref.16 Ref.26 Ref.27 Ref.29Genetic variations in APOE are associated with Alzheimer disease type 2 (AD2) [ MIM:104310]. It is a late-onset neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitive abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituent of these plaques is the neurotoxic amyloid-beta-APP 40-42 peptide (s), derived proteolytically from the transmembrane precursor protein APP by sequential secretase processing. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products such as C31 derived from APP, are also implicated in neuronal death. Note=The APOE*4 allele is genetically associated with the common late onset familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer disease. Risk for AD increased from 20% to 90% and mean age at onset decreased from 84 to 68 years with increasing number of APOE*4 alleles in 42 families with late onset AD. Thus APOE*4 gene dose is a major risk factor for late onset AD and, in these families, homozygosity for APOE*4 was virtually sufficient to cause AD by age 80. The mechanism by which APOE*4 participates in pathogenesis is not known. Ref.16Defects in APOE are a cause of sea-blue histiocyte disease (SBHD) [ MIM:269600]; also known as sea-blue histiocytosis. This disorder is characterized by splenomegaly, mild thrombocytopenia and, in the bone marrow, numerous histiocytes containing cytoplasmic granules which stain bright blue with the usual hematologic stains. The syndrome is the consequence of an inherited metabolic defect analogous to Gaucher disease and other sphingolipidoses. Ref.16 Ref.33 Ref.36Defects in APOE are a cause of lipoprotein glomerulopathy (LPG) [ MIM:611771]. LPG is an uncommon kidney disease characterized by proteinuria, progressive kidney failure, and distinctive lipoprotein thrombi in glomerular capillaries. It mainly affects people of Japanese and Chinese origin. The disorder has rarely been described in Caucasians. Ref.16 Ref.30 Ref.32 Ref.37 Sequence similarities: Belongs to the apolipoprotein A1/A4/E family. |
| NCBI Summary: | Chylomicron remnants and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) remnants are rapidly removed from the circulation by receptor-mediated endocytosis in the liver. Apolipoprotein E, a main apoprotein of the chylomicron, binds to a specific receptor on liver cells and peripheral cells. ApoE is essential for the normal catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein constituents. The APOE gene is mapped to chromosome 19 in a cluster with APOC1 and APOC2. Defects in apolipoprotein E result in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, or type III hyperlipoproteinemia (HLP III), in which increased plasma cholesterol and triglycerides are the consequence of impaired clearance of chylomicron and VLDL remnants. [provided by RefSeq] |
| UniProt Code: | P02649 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 114039 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 348 |
| NCBI Accession: | P02649.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P02649,Q9P2S4, B2RC15, C0JYY5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P02649,Q13791,Q6LA97,Q6LBZ1,Q8TCZ8 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Apolipoprotein E |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | apolipoprotein E |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | APOE |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AD2; LPG; LDLCQ5; MGC1571 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | apolipoprotein E; apo-E; apolipoprotein E3; OTTHUMP00000159143; OTTHUMP00000197075; OTTHUMP00000197076; OTTHUMP00000197077 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Apolipoprotein E |
| Protein Family: | Apolipoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | APOE |
| UniProt Entry Name: | APOE_HUMAN |
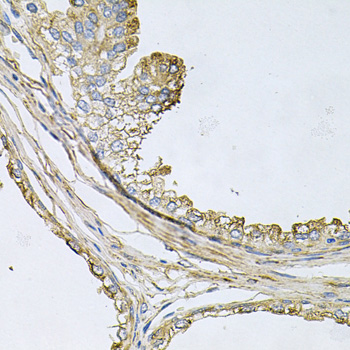 | Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human prostate using ApoE antibody (CAB12400) at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens). |