| UniProt Protein Function: | AMPKA2: a catalytic subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Acts as an energy sensor, playing a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism. A protein kinase of the CAMKL family whose activation is regulated by the balance between ADP/AMP/ATP, and intracellular Ca(2+) levels. Acts as a metabolic stress-sensing protein kinase switching off biosynthetic pathways when cellular ATP levels are depleted and when 5'-ADP and -AMP rise in response to fuel limitation and/or hypoxia. Activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes. Restores ATP levels in cells by switching off anabolic and switching on catabolic pathways. Activated primarily by rising ADP levels and not, as previously thought, solely by AMP. AMPK resembles an adenylate charge regulatory system in which anabolic and catabolic pathways are regulated by adenine nucleotide ratios. Acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes and transcription regulators. Regulates fatty acid synthesis by phosphorylating acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Regulates cholesterol synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating hormone-sensitive lipase and hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase. Activated by at least two distinct upstream kinases: the tumor suppressor LKB1 and CaMKK2. Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton, probably by indirectly activating myosin. AMPK is a heterotrimer of an alpha catalytic subunit (AMPKA1 or -2), a beta (AMPKB1 or -2) and a gamma non-catalytic subunit (AMPKG1, -2 or -3). Different possible combinations of subunits give rise to 12 different holoenzymes. Binding of ADP or AMP to non-catalytic gamma subunit (PRKAG1, -2 or -3) results in allosteric activation. AMPK is activated by antihyperglycemic drug metformin, a drug prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes: in vivo, metformin seems to mainly inhibit liver gluconeogenesis. However, metformin can be used to activate AMPK in muscle and other cells in culture or ex vivo. Selectively inhibited by compound C (6-[4-(2-Piperidin-1-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl)]-3-pyridin-4-yl-pyyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidine. Activated by resveratrol, a natural polyphenol present in red wine, and S17834, a synthetic polyphenol. Salicylate/aspirin directly activates kinase activity. Studies in the mouse suggest that AMPK2 may control whole-body insulin sensitivity and is necessary for maintaining myocardial energy homeostasis during ischemia. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 2.7.11.31; EC 2.7.11.1; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Autophagy; Kinase, protein; Protein kinase, CAMK; EC 2.7.11.27; CAMK group; CAMKL family; AMPK subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p31 Cellular Component: AMP-activated protein kinase complex; cytoplasm; cytosol; nucleoplasm Molecular Function:[acetyl-CoA carboxylase] kinase activity; [hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH)] kinase activity; AMP-activated protein kinase activity; ATP binding; chromatin binding; histone serine kinase activity; metal ion binding; protein binding; protein kinase activity; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity Biological Process: carnitine shuttle; cell cycle arrest; cellular lipid metabolic process; cellular response to glucose starvation; cellular response to nutrient levels; cholesterol biosynthetic process; energy reserve metabolic process; fatty acid biosynthetic process; fatty acid homeostasis; gene expression; glucose homeostasis; insulin receptor signaling pathway; lipid biosynthetic process; macroautophagy; mitochondrion organization and biogenesis; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of TOR signaling pathway; organelle organization and biogenesis; positive regulation of autophagy; positive regulation of glycolysis; positive regulation of macroautophagy; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of circadian rhythm; regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process; regulation of macroautophagy; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; response to muscle activity; response to stress; rhythmic process; signal transduction; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; Wnt receptor signaling pathway |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a catalytic subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic beta and gamma subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. Studies of the mouse counterpart suggest that this catalytic subunit may control whole-body insulin sensitivity and is necessary for maintaining myocardial energy homeostasis during ischemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P54646 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 20178276 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5563 |
| NCBI Accession: | P54646.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P54646,Q9H1E8, Q9UD43, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P54646,AAB32732 |
| Molecular Weight: | 62,320 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PRKAA2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AMPK; AMPK2; PRKAA; AMPKa2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase (EC:2.7.11.27 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PRKAA2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | AAPK2_HUMAN |
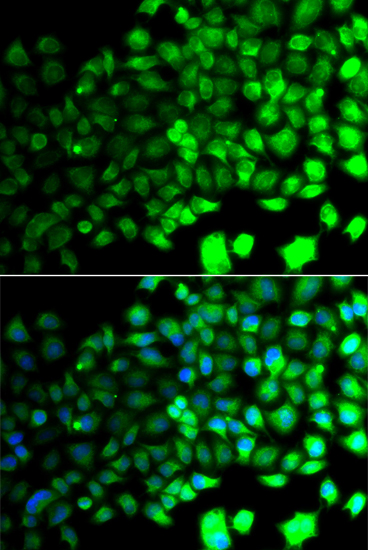

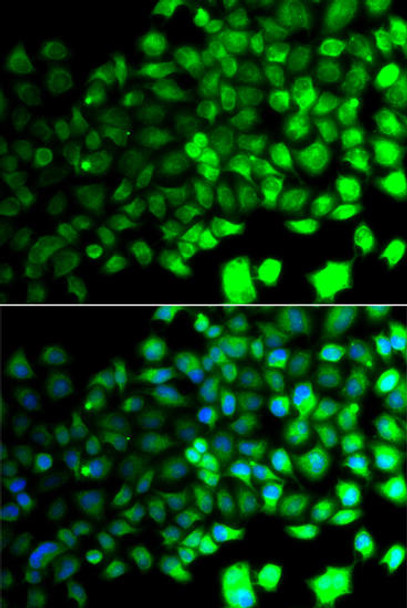
![Anti-AMPKAlpha2 Antibody (CAB7339)[KO Validated] Anti-AMPKAlpha2 Antibody (CAB7339)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/47531/52275/anti-ampkalpha2-antibody-cab7339ko-validated__96839__62605.1706525456.jpg?c=1)



