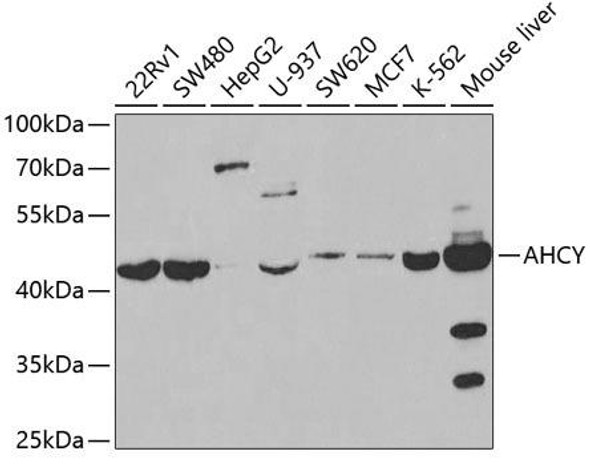
Description
| Product Name: | AHCY Rabbit mAb |
| Product Code: | CAB2756 |
| Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Synonyms: | AHCY, SAHH, adoHcyase, adenosylhomocysteinase |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human AHCY. |
| Applications: | WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HT-29, HepG2, A375, K-562, Mouse pancreas, Mouse liver, Mouse kidney, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human AHCY. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 191 |
| Uniprot: | P23526 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Melanosome |
| Calculated MW: | 47kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45KDa |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SAHH: Adenosylhomocysteine is a competitive inhibitor of S- adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyl transferase reactions; therefore adenosylhomocysteinase may play a key role in the control of methylations via regulation of the intracellular concentration of adenosylhomocysteine. Defects in AHCY are the cause of hypermethioninemia with S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency (HMAHCHD). A metabolic disorder characterized by hypermethioninemia associated with failure to thrive, mental and motor retardation, facial dysmorphism with abnormal hair and teeth, and myocardiopathy. Belongs to the adenosylhomocysteinase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Other Amino Acids Metabolism - selenoamino acid; Amino Acid Metabolism - cysteine and methionine; EC 3.3.1.1; Hydrolase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 20q11.22 Cellular Component: neuron projection; cytoplasm; melanosome; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:identical protein binding; adenyl nucleotide binding; adenosylhomocysteinase activity Biological Process: methylation; circadian sleep/wake cycle; S-adenosylmethionine cycle; sulfur amino acid metabolic process; xenobiotic metabolic process; response to hypoxia; S-adenosylhomocysteine catabolic process; one-carbon compound metabolic process; chronic inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus; response to nutrient Disease: Hypermethioninemia With S-adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase belongs to the adenosylhomocysteinase family. It catalyzes the reversible hydrolysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy) to adenosine (Ado) and L-homocysteine (Hcy). Thus, it regulates the intracellular S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) concentration thought to be important for transmethylation reactions. Deficiency in this protein is one of the different causes of hypermethioninemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P23526 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 20141702 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 191 |
| NCBI Accession: | P23526.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P23526,Q96A36, A8K307, B3KUN3, E1P5P2, F5H737, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P23526 |
| Molecular Weight: | 432 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Adenosylhomocysteinase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | adenosylhomocysteinase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | AHCY |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SAHH; adoHcyase |
| NCBI Protein Information: | adenosylhomocysteinase; S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Adenosylhomocysteinase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase |
| Protein Family: | Adenosylhomocysteinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | AHCY |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SAHH_HUMAN |