Signal Transduction Antibodies 1
Anti-ACTL7B Antibody (CAB13149)
- SKU:
- CAB13149
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ACTL7B Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB13149 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
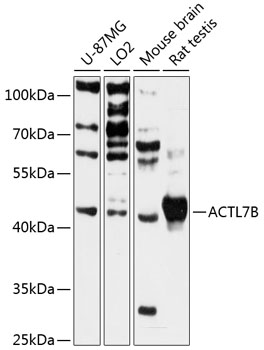
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 200-380 of human ACTL7B (NP_006677.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:1000 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | U-87MG, LO2, Mouse brain, Rat testis |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 200-380 of human ACTL7B (NP_006677.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | GHGV SHVV PISE GDVL PGLT SRAD YAGG DLTN YLMQ LLNE AGHA FTDD HLHI IEHI KKKC CYAA FLPE EELG LVPE ELRV DYEL PDGK LITI GQER FRCS EMLF QPSL AGST QPGL PELT AACL GRCQ DTGF KEEM AANV LLCG GCTM LDGF PERF QREL SLLC PGDS PAVA AAPE RKTS V |
| Gene ID: | 10880 |
| Uniprot: | Q9Y614 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton |
| Calculated MW: | 45kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45kDa |
| Synonyms: | ACTL7B, Tact1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family of actin-related proteins (ARPs) which share significant amino acid sequence identity to conventional actins. Both actins and ARPs have an actin fold, which is an ATP-binding cleft, as a common feature. The ARPs are involved in diverse cellular processes, including vesicular transport, spindle orientation, nuclear migration and chromatin remodeling. This gene (ACTL7B), and related gene, ACTL7A, are intronless, and are located approximately 4 kb apart in a head-to-head orientation within the familial dysautonomia candidate region on 9q31. Based on mutational analysis of the ACTL7B gene in patients with this disorder, it was concluded that it is unlikely to be involved in the pathogenesis of dysautonomia. Unlike ACTL7A, the ACTL7B gene is expressed predominantly in the testis, however, its exact function is not known. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ACTL7B: is a member of a family of actin-related proteins (ARPs) which share significant amino acid sequence identity to conventional actins. Both actins and ARPs have an actin fold, which is an ATP-binding cleft, as a common feature. The ARPs are involved in diverse cellular processes, including vesicular transport, spindle orientation, nuclear migration and chromatin remodeling. This gene (ACTL7B), and related gene, ACTL7A, are intronless, and are located approximately 4 kb apart in a head-to-head orientation within the familial dysautonomia candidate region on 9q31. Based on mutational analysis of the ACTL7B gene in patients with this disorder, it was concluded that it is unlikely to be involved in the pathogenesis of dysautonomia. Unlike ACTL7A, the ACTL7B gene is expressed predominantly in the testis, however, its exact function is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cytoskeletal; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9q31 Cellular Component: actin cytoskeleton Molecular Function:structural constituent of cytoskeleton |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family of actin-related proteins (ARPs) which share significant amino acid sequence identity to conventional actins. Both actins and ARPs have an actin fold, which is an ATP-binding cleft, as a common feature. The ARPs are involved in diverse cellular processes, including vesicular transport, spindle orientation, nuclear migration and chromatin remodeling. This gene (ACTL7B), and related gene, ACTL7A, are intronless, and are located approximately 4 kb apart in a head-to-head orientation within the familial dysautonomia candidate region on 9q31. Based on mutational analysis of the ACTL7B gene in patients with this disorder, it was concluded that it is unlikely to be involved in the pathogenesis of dysautonomia. Unlike ACTL7A, the ACTL7B gene is expressed predominantly in the testis, however, its exact function is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9Y614 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 27923724 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 10880 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9Y614.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9Y614,Q5JSV1, B2R9Q2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9Y614 |
| Molecular Weight: | 45,234 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Actin-like protein 7B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | actin like 7B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ACTL7B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | Tact1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | actin-like protein 7B |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Actin-like protein 7B |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Actin-like-7-beta |
| Protein Family: | Actin-like protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ACTL7B |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ACL7B_HUMAN |
View AllClose