Description
Assay Genie's alpha-amylase assay method involves two steps: (1). alpha-amylase in the sample hydrolyzes starch and the product is rapidly converted to glucose by alpha-glucosidase and hydrogen peroxide by glucose oxidase; (2). hydrogen peroxide concentration is determined with a colorimetric reagent.
Applications
For quantitative determination of alpha-amylase activity
Key Features
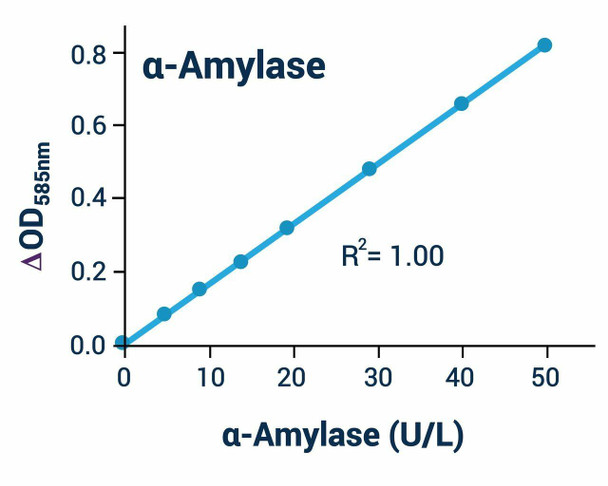
- Sensitive and accurate. Linear detection range 0.3 to 50 U/L alpha-amylase in 96-well plate assay.
- Convenient. The procedure involves adding a single working reagent, incubation for 15 min, followed by the detection reagent and a 20-min incubation and reading the optical density at 585 nm.
Data Sheet | |
| Kit Includes | Assay Buffer (pH 7.0): 20 mL Substrate: 120 mL Detection Reagent: 20 mL Enzyme A: 120 mL Glucose Standard: 1 mL Enzyme B: 120 mL |
| Kit Requires | Pipeting devices, centrifuge tubes, clear flat-bottom 96-well plates, plate reader, and optionally membrane filters. |
| Method of Detection | OD585nm |
| Detection Limit | 0.3 U/L |
| Samples | Blood, saliva, urine, agriculture etc |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 40 min |
| Size | 100 tests |
| Storage | Store Detection Reagent at 4°C and others at -20°C |
| Shelf Life | 6 months |
More Details
AMYLASE belongs to the family of glycoside hydrolase enzymes that break down starch into glucose molecules by acting on alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds. The alpha-amylases (EC 3.2.1.1) cleave at random locations on the starch chain, ultimately yielding maltotriose and maltose, glucose and "limit dextrin" from amylose and amylopectin. In mammals, alpha-amylase is a major digestive enzyme. Increased enzyme levels in humans are associated with salivary trauma, mumps due to inflammation of the salivary glands, pancreatitis and renal failure. Simple, direct and automation-ready procedures for measuring amylase activity are very desirable.