Description
| Product Name: | Recombinant Human DC-SIGN/CD209 (N-Fc) |
| Product Code: | RPES6337 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 Cells |
| Synonyms: | CD209 molecule, CD209, CDSIGNHIV gpl20-binding protein, CLEC4L, DCSIGN, DC-SIGN, DC-SIGN1, CD209 Antigen |
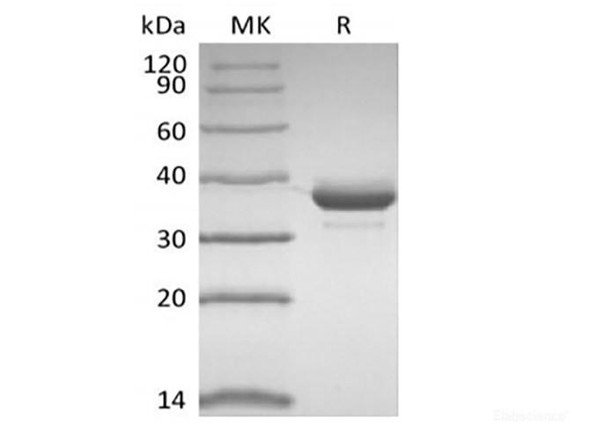
| Mol Mass: | 65.3 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 75 kDa |
| Tag: | N-Fc |
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | Gln59-Ala404 |
| Accession: | Q9NNX6 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the printed manual. |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | CD209 is also known as CLEC4L, DC-SIGN and CD209 antigen, is a type II transmembrane protein on DCs with a C-type lectin extracellular domain, is capable of binding ICAM-3 on resting T cells in the secondary lymphoid organs, providing the initial contact between these cells during the establishment of cell-mediated immunity. The DC-SIGN/CD209 lectin domain binds mannose oligosaccharides on pathogens including HIV as well as self glycoproteins including ICAMs (2, 4). DC-SIGN/CD209 binds to butyrophilin 2A1 and this interaction can be blocked by HIV pp120. DC-SIGN/CD209 is expressed on dendritic cells (DC) and inflammatory macrophages and contributes to antigen presentation. It is not only a pattern recognition receptor but implicated in immunoregulation of DCs. It has important role in mediating DC adhesion, migration, inflammation, activating primary T cell, triggering immune response and participating in immune escape of pathogens and tumors. |