Description
| Antibody Name: | MYH6/MYH7 Antibody (PACO07425) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO07425 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:10000-1:20000, IHC-p:1:50-1:300 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 1871-1920 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
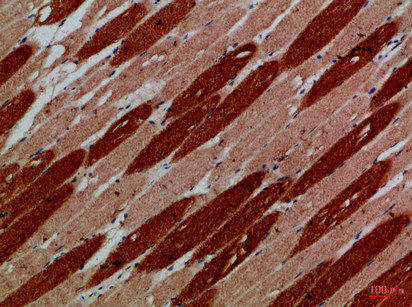 | Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-skeletal-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100. |
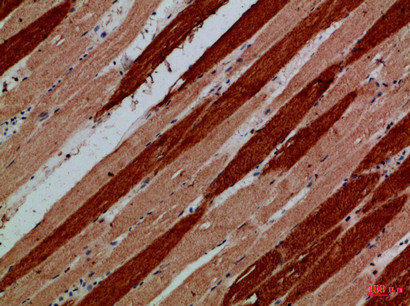 | Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-skeletal-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100. |
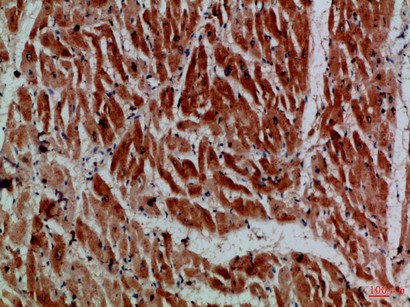 | Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-heart, antibody was diluted at 1:100. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | MYH6: Muscle contraction. Defects in MYH6 are the cause of atrial septal defect type 3 (ASD3). ASD3 is a congenital heart malformation characterized by incomplete closure of the wall between the atria resulting in blood flow from the left to the right atria. Defects in MYH6 are the cause of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy type 14 (CMH14). It is a hereditary heart disorder characterized by ventricular hypertrophy, which is usually asymmetric and often involves the interventricular septum. The symptoms include dyspnea, syncope, collapse, palpitations,and chest pain. They can be readily provoked by exercise. The disorder has inter- and intrafamilial variability ranging from benign to malignant forms with high risk of cardiac failure and sudden cardiac death. Defects in MYH6 are the cause of cardiomyopathy dilated type 1EE (CMD1EE). It is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death. Defects in MYH6 are the cause of susceptibility to sick sinus syndrome type 3 (SSS3). The term 'sick sinus syndrome' encompasses a variety of conditions caused by sinus node dysfunction. The most common clinical manifestations are syncope, presyncope, dizziness, and fatigue. Electrocardiogram typically shows sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, and/or sinoatrial block. Episodes of atrial tachycardias coexisting with sinus bradycardia ('tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome') are also common in this disorder. SSS occurs most often in the elderly associated with underlying heart disease or previous cardiac surgery, but can also occur in the fetus, infant, or child without heart disease or other contributing factors. MYH6 variations are associated with susceptibility to sick sinus syndrome (PubMed:21378987). The lifetime risk of being diagnosed with sick sinus syndrome is higher for carriers of variant p.Arg721Trp than for non-carriers (PubMed:21378987). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motor; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q12 Cellular Component: cytosol; muscle myosin complex; myofibril; myosin complex; sarcomere Molecular Function:actin-dependent ATPase activity; ATPase activity; microfilament motor activity; myosin phosphatase activity; protein kinase binding Biological Process: adult heart development; ATP metabolic process; atrial cardiac muscle morphogenesis; cardiac muscle contraction; cardiac muscle fiber development; in utero embryonic development; muscle contraction; muscle filament sliding; myofibril assembly; regulation of ATPase activity; regulation of blood pressure; regulation of heart contraction; regulation of heart rate; regulation of the force of heart contraction; sarcomere organization; striated muscle contraction; ventricular cardiac muscle morphogenesis; visceral muscle development Disease: Atrial Septal Defect 3; Cardiomyopathy, Dilated, 1ee; Cardiomyopathy, Familial Hypertrophic, 1; Cardiomyopathy, Familial Hypertrophic, 14; Sick Sinus Syndrome 3, Susceptibility To |
| NCBI Summary: | Cardiac muscle myosin is a hexamer consisting of two heavy chain subunits, two light chain subunits, and two regulatory subunits. This gene encodes the alpha heavy chain subunit of cardiac myosin. The gene is located ~4kb downstream of the gene encoding the beta heavy chain subunit of cardiac myosin. Mutations in this gene cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and atrial septal defect 3. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P13533 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 317373582 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4624 |
| NCBI Accession: | P13533.5 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P13533,Q13943, Q14906, Q14907, A2RTX1, D9YZU2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P13533 |
| Molecular Weight: | 223,735 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Myosin-6 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | myosin heavy chain 6 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MYH6 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ASD3; MYHC; SSS3; CMH14; MYHCA; CMD1EE; alpha-MHC |
| NCBI Protein Information: | myosin-6 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Myosin-6 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Myosin heavy chain 6; Myosin heavy chain, cardiac muscle alpha isoform; MyHC-alpha |
| Protein Family: | Myosin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MYH6 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MYH6_HUMAN |






