Mouse Cell Signalling ELISA Kits 2
Mouse GDF1 (Growth Differentiation Factor 1) CLIA Kit (MOES00314)
- SKU:
- MOES00314
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- CLIA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Sensitivity:
- 7.5pg/mL
- Range:
- 12.5-800pg/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
Description
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Detection method: | Chemiluminescence |
| Detection range: | 12.50-800 pg/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 7.50 pg/mL |
| Sample volume: | 100µL |
| Sample type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Repeatability: | CV < 15% |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Mouse GDF1 in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Mouse GDF1 and analogues was observed. |
This kit uses Sandwich-CLIA as the method. The micro CLIA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Mouse GDF1. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro CLIA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Mouse GDF1 and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Mouse GDF1, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear fluorescence. The Relative light unit (RLU) value is measured spectrophotometrically by the Chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. The RLU value is positively associated with the concentration of Mouse GDF1. The concentration of Mouse GDF1 in the samples can be calculated by comparing the RLU of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | GDF1: May mediate cell differentiation events during embryonic development. Defects in GDF1 are a cause of conotruncal heart malformations (CTHM). A group of congenital heart defects involving the outflow tracts. Examples include truncus arteriosus communis, double-outlet right ventricle and transposition of great arteries. Truncus arteriosus communis is characterized by a single outflow tract instead of a separate aorta and pulmonary artery. In transposition of the great arteries, the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle. In double outlet of the right ventricle, both the pulmonary artery and aorta arise from the right ventricle. Defects in GDF1 are the cause of transposition of the great arteries dextro-looped type 3 (DTGA3). A congenital heart defect consisting of complete inversion of the great vessels, so that the aorta incorrectly arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery incorrectly arises from the left ventricle. This creates completely separate pulmonary and systemic circulatory systems, an arrangement that is incompatible with life. The presence or absence of associated cardiac anomalies defines the clinical presentation and surgical management of patients with transposition of the great arteries. Defects in GDF1 are a cause of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). A congenital heart anomaly which consists of pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, dextroposition of the aorta (aorta is on the right side instead of the left) and hypertrophy of the right ventricle. In this condition, blood from both ventricles (oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor) is pumped into the body often causing cyanosis. Belongs to the TGF-beta family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; Secreted Cellular Component: extracellular space Molecular Function:cytokine activity; transforming growth factor beta receptor binding Biological Process: BMP signaling pathway; regulation of apoptosis; in utero embryonic development; regulation of MAPKKK cascade; mesoderm development; signal transduction; cell development; endoderm development |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family and the TGF-beta superfamily. This group of proteins is characterized by a polybasic proteolytic processing site that is cleaved to produce a mature protein containing seven conserved cysteine residues. The members of this family are regulators of cell growth and differentiation in both embryonic and adult tissues. This protein is involved in the establishment of left-right asymmetry in early embryogenesis and in neural development in later embryogenesis. This protein is transcribed from a monocistronic mRNA early in development, and from a bicistronic mRNA in later stages that also encodes the LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 1 gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P20863 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 253970469 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 14559 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_001156754. 1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P20863,Q6AXH1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P20863 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | embryonic growth/differentiation factor 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | growth differentiation factor 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Gdf1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | Gdf-1; AI385651 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | embryonic growth/differentiation factor 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Embryonic growth/differentiation factor 1 |
| Protein Family: | Embryonic growth/differentiation factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Gdf1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GDF1_MOUSE |
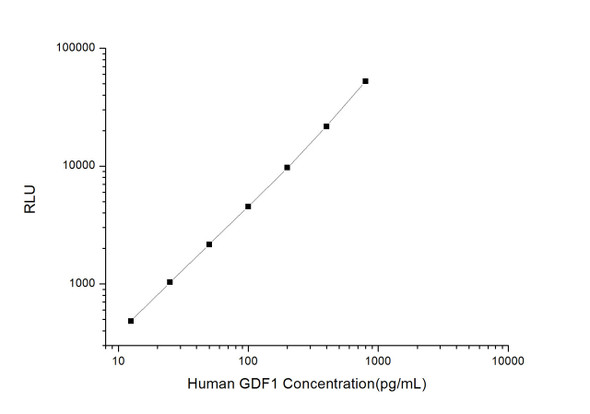
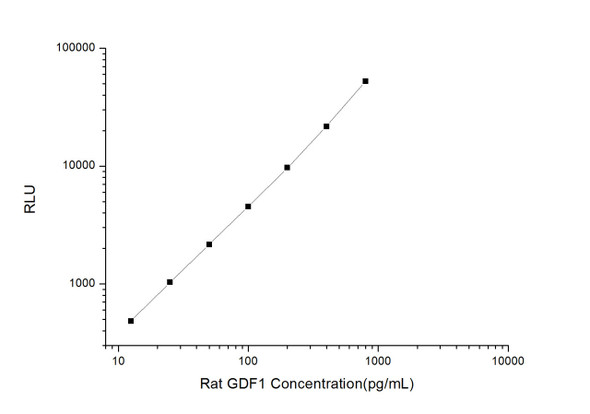
As the RLU values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU | Average | Corrected |
| 800 | 50324 54960 | 52642 | 52616 |
| 400 | 20738 22730 | 21734 | 21708 |
| 200 | 10525 8891 | 9708 | 9682 |
| 100 | 4443 4661 | 4552 | 4526 |
| 50 | 2208 2168 | 2188 | 2162 |
| 25 | 1092 1028 | 1060 | 1034 |
| 12.50 | 481 537 | 509 | 483 |
| 0 | 25 27 | 26 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Mouse GDF1 were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Mouse GDF1 were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 38.86 | 92.23 | 300.54 | 35.59 | 94.65 | 298.06 |
| Standard deviation | 4.30 | 6.83 | 26.39 | 4.04 | 9.28 | 32.31 |
| C V (%) | 11.07 | 7.41 | 8.78 | 11.35 | 9.80 | 10.84 |
Recovery
The recovery of Mouse GDF1 spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 86-101 | 92 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 92-104 | 97 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 86-98 | 93 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Mouse GDF1 and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 94-106 | 89-100 | 96-111 |
| Average (%) | 101 | 94 | 103 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 99-115 | 89-103 | 96-112 |
| Average (%) | 106 | 96 | 104 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 89-104 | 91-104 | 90-105 |
| Average (%) | 95 | 98 | 96 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 93-105 | 86-100 | 96-108 |
| Average (%) | 98 | 91 | 102 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro CLIA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent A | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Substrate Reagent B | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100µl of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100µl of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100µl of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids. ) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 100µL of Substrate mixture solution to each well. Cover with a new plate seal andincubate for no more than 5 min at 37°C. Protect the plate from light.
- Determine the RLU value of each well immediately.