Description
| Product Name: | Human SUMO2 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB4879 |
| Size: | 50µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | SUMO2 |
| Synonyms: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2, SUMO-2, Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3B, SMT3 homolog 2, Sentrin-2, HSMT3, SUMO-3, SUMO2, SMT3B, SMT3H2, MGC117191. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | The SUMO2 (1mg/ml) containing 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0). |
| Stability: | Can be stored at +4C for 1 week. For long term storage , below -20C.Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
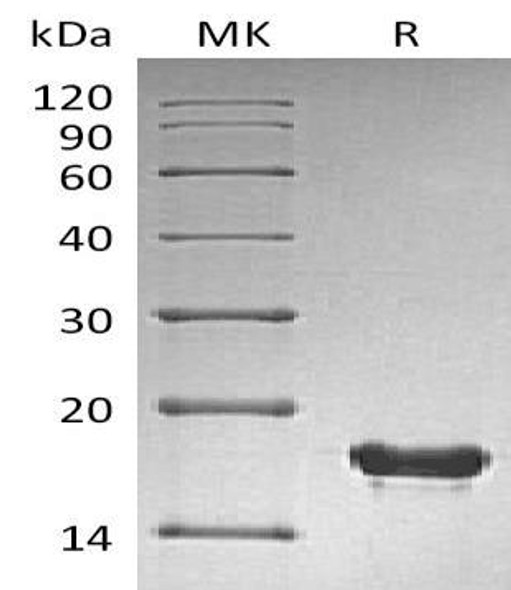
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MADEKPKEGVKTENNDHINLKVAGQDGSVVQFKIKRHTPLSKLMKAYCERQGLSMRQIRFRFDGQPINETDTPAQLEMEDEDTIDVFQQQTGG |
Small Ubiquitin-like Modifiers (SUMOs) are a family of small, related proteins that can be enzymatically attached to a target protein by a post-translational modification process termed sumoylation. Unlike ubiquitination, which targets proteins for degradation, sumoylation participates in a number of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability. All SUMO proteins share the conserved ubiquitin domain and the C-terminal diglycine cleavage/attachment site. Human SUMO2, also known as Sentrin2 and SMT3B is synthesized as a 95 amino acid (aa), 11 kDa propeptide that contains a two aa C-terminal prosegment, and an 18 aa N-terminal protein interacting region (aa 33 -50). Following prosegment cleavage, the C-terminal glycine is enzymatically attached to a lysine on a target protein. Human SUMO2 shares 100% sequence identity to SUMO-2 from mouse. SUMO2 also has very high sequence homology to SUMO3 and SUMO4, 86 % and 85%, respectively. SUMO2 shares only 44% sequence identity to SUMO1.
SUMO2 Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 93 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 10.6 kDa.The SUMO-2 is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | SUMO2: Ubiquitin-like protein that can be covalently attached to proteins as a monomer or as a lysine-linked polymer. Covalent attachment via an isopeptide bond to its substrates requires prior activation by the E1 complex SAE1-SAE2 and linkage to the E2 enzyme UBE2I, and can be promoted by an E3 ligase such as PIAS1-4, RANBP2 or CBX4. This post-translational modification on lysine residues of proteins plays a crucial role in a number of cellular processes such as nuclear transport, DNA replication and repair, mitosis and signal transduction. Polymeric SUMO2 chains are also susceptible to polyubiquitination which functions as a signal for proteasomal degradation of modified proteins. Homotrimer (Potential). Crystal packing analysis suggests a possible trimeric assembly, of which the biological significance remains to be determined. Interacts with SAE2 and UBE2I. Covalently attached to a number of proteins. Interacts with PELP1. Interacts with USP25; the interaction sumoylates USP25. Broadly expressed. Belongs to the ubiquitin family. SUMO subfamily. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Ubiquitin-like modifier Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q25.1 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; PML body; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding Biological Process: protein sumoylation; cellular protein metabolic process; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; post-translational protein modification |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) protein family. It functions in a manner similar to ubiquitin in that it is bound to target proteins as part of a post-translational modification system. However, unlike ubiquitin which targets proteins for degradation, this protein is involved in a variety of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability. It is not active until the last two amino acids of the carboxy-terminus have been cleaved off. Numerous pseudogenes have been reported for this gene. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P61956 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 378405233 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6613 |
| NCBI Accession: | P61956.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P61956,P55855, Q32Q42, Q6IPZ6, Q96HK1, B2R4I2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P61956 |
| Molecular Weight: | 95 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | small ubiquitin-like modifier 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SUMO2�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HSMT3; SMT3B; SUMO3; Smt3A; SMT3H2�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | small ubiquitin-related modifier 2; sentrin 2; SMT3 homolog 2; ubiquitin-like protein SMT3A; ubiquitin-like protein SMT3B; SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | HSMT3; SMT3 homolog 2; SUMO-3; Sentrin-2; Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3B |
| Protein Family: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SUMO2�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SUMO2_HUMAN |