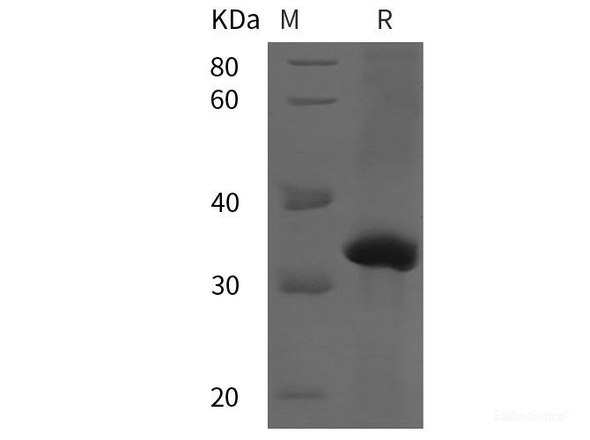
Description
| Product Name: | Human CDK4 Recombinant Protein (His Tag) |
| Product Code: | RPES6523 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | E.coli |
| Synonyms: | Cdk 4,cdk4,CDK4 protein,CDK4,Cell division kinase 4,Cell division protein kinase 4,CMM 3,CMM3,Crk3,Cyclin dependent kinase 4,Cyclin-dependent kinase 4,Melanoma cutaneous malignant 3,MGC14458,p34 cdk4,PSK J3,PSK-J3 |
| Application: | Immunogen |
| Mol Mass: | 33.5 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 35.8 kDa |
| Tag: | N-His |
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | Please contact us for more information. |
| Bio Activity: | Immunogen |
| Sequence: | Ala2-Glu303 |
| Accession: | P11802-1 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the printed manual. |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Mutations in this gene as well as in its related proteins including D-type cyclins, p16(INK4a) and Rb were all found to be associated with tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers. Multiple polyadenylation sites of this gene have been reported. |