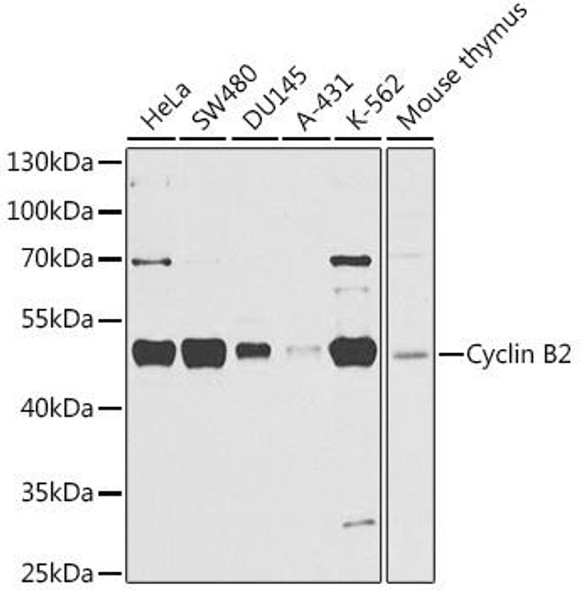
Description
| Antibody Name: | Hbb-b2 Antibody (PACO34810) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO34810 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA |
| Recommended Dilutions: | |
| Species Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Mouse Hemoglobin subunit beta-2 protein (2-147AA) |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 |
| Purification Method: | >95%, Protein G purified |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Synonyms: | Hemoglobin subunit beta-2 (Beta-2-globin) (Hemoglobin beta-2 chain) (Hemoglobin beta-minor chain), Hbb-b2 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HBB: Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues. Defects in HBB may be a cause of Heinz body anemias (HEIBAN). This is a form of non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia of Dacie type 1. After splenectomy, which has little benefit, basophilic inclusions called Heinz bodies are demonstrable in the erythrocytes. Before splenectomy, diffuse or punctate basophilia may be evident. Most of these cases are probably instances of hemoglobinopathy. The hemoglobin demonstrates heat lability. Heinz bodies are observed also with the Ivemark syndrome (asplenia with cardiovascular anomalies) and with glutathione peroxidase deficiency. Defects in HBB are the cause of beta-thalassemia (B-THAL). A form of thalassemia. Thalassemias are common monogenic diseases occurring mostly in Mediterranean and Southeast Asian populations. The hallmark of beta-thalassemia is an imbalance in globin-chain production in the adult HbA molecule. Absence of beta chain causes beta(0)-thalassemia, while reduced amounts of detectable beta globin causes beta(+)-thalassemia. In the severe forms of beta-thalassemia, the excess alpha globin chains accumulate in the developing erythroid precursors in the marrow. Their deposition leads to a vast increase in erythroid apoptosis that in turn causes ineffective erythropoiesis and severe microcytic hypochromic anemia. Clinically, beta-thalassemia is divided into thalassemia major which is transfusion dependent, thalassemia intermedia (of intermediate severity), and thalassemia minor that is asymptomatic. Defects in HBB are the cause of sickle cell anemia (SKCA); also known as sickle cell disease. Sickle cell anemia is characterized by abnormally shaped red cells resulting in chronic anemia and periodic episodes of pain, serious infections and damage to vital organs. Normal red blood cells are round and flexible and flow easily through blood vessels, but in sickle cell anemia, the abnormal hemoglobin (called Hb S) causes red blood cells to become stiff. They are C-shaped and resembles a sickle. These stiffer red blood cells can led to microvascular occlusion thus cutting off the blood supply to nearby tissues. Defects in HBB are the cause of beta-thalassemia dominant inclusion body type (B-THALIB). An autosomal dominant form of beta thalassemia characterized by moderate anemia, lifelong jaundice, cholelithiasis and splenomegaly, marked morphologic changes in the red cells, erythroid hyperplasia of the bone marrow with increased numbers of multinucleate red cell precursors, and the presence of large inclusion bodies in the normoblasts, both in the marrow and in the peripheral blood after splenectomy. Belongs to the globin family.Protein type: CarrierChromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11p15.5Cellular Component: hemoglobin complex; extracellular region; cytosolMolecular Function: haptoglobin binding; protein binding; peroxidase activity; hemoglobin binding; iron ion binding; heme binding; oxygen binding; oxygen transporter activityBiological Process: receptor-mediated endocytosis; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process; nitric oxide transport; response to hydrogen peroxide; oxygen transport; protein heterooligomerization; bicarbonate transport; hydrogen peroxide catabolic process; regulation of blood pressure; blood coagulation; regulation of blood vessel sizeDisease: Fetal Hemoglobin Quantitative Trait Locus 1; Beta-thalassemia; Sickle Cell Anemia; Heinz Body Anemias; Beta-thalassemia, Dominant Inclusion Body Type; Malaria, Susceptibility To; Alpha-thalassemia |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | The alpha (HBA) and beta (HBB) loci determine the structure of the 2 types of polypeptide chains in adult hemoglobin, Hb A. The normal adult hemoglobin tetramer consists of two alpha chains and two beta chains. Mutant beta globin causes sickle cell anemia. Absence of beta chain causes beta-zero-thalassemia. Reduced amounts of detectable beta globin causes beta-plus-thalassemia. The order of the genes in the beta-globin cluster is 5'-epsilon -- gamma-G -- gamma-A -- delta -- beta--3'. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P02089 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 56749856 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3043 |
| NCBI Accession: | P68871.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P02089,P04246, P02101, P02128, P06643, P06642, P02042 P02057, P02112, P02081 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P02089,P68871 |
| Molecular Weight: | 15998 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Hemoglobin subunit beta |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | hemoglobin subunit beta |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HBB |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ECYT6; CD113t-C; beta-globin |
| NCBI Protein Information: | hemoglobin subunit beta |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Hemoglobin subunit beta |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Beta-globin; Hemoglobin beta chainCleaved into the following 2 chains:LVV-hemorphin-7; Spinorphin |
| Protein Family: | Hemoglobin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HBB |
| UniProt Entry Name: | HBB_HUMAN |