Description
| Antibody Name: | EYA1/EYA4 Antibody (PACO07423) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO07423 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:10000-1:20000, IHC-p:1:50-1:300 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 271-320 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
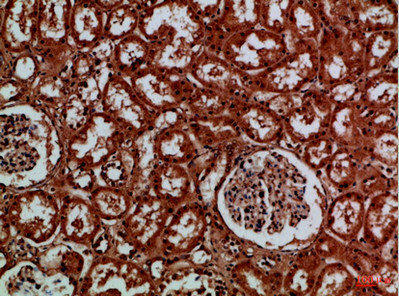 | Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-kidney, antibody was diluted at 1:100. |
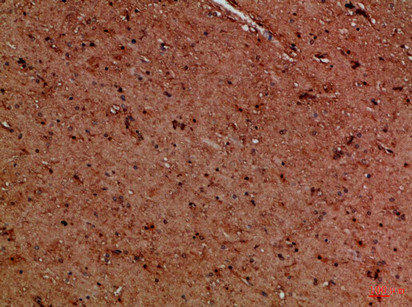 | Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-brain, antibody was diluted at 1:100. |
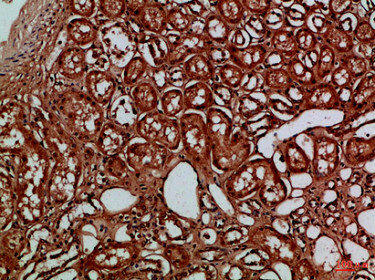 | Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-kidney, antibody was diluted at 1:100. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | EYA1: Tyrosine phosphatase that specifically dephosphorylates 'Tyr-142' of histone H2AX (H2AXY142ph). 'Tyr-142' phosphorylation of histone H2AX plays a central role in DNA repair and acts as a mark that distinguishes between apoptotic and repair responses to genotoxic stress. Promotes efficient DNA repair by dephosphorylating H2AX, promoting the recruitment of DNA repair complexes containing MDC1. Its function as histone phosphatase probably explains its role in transcription regulation during organogenesis. Seems to coactivate SIX2, SIX4 and SIX5. May be required for normal development of branchial arches, ear and kidney. Defects in EYA1 are the cause of branchiootorenal syndrome type 1 (BOR1); also known as Melnick-Fraser syndrome. BOR is an autosomal dominant disorder manifested by various combinations of preauricular pits, branchial fistulae or cysts, lacrimal duct stenosis, hearing loss, structural defects of the outer, middle, or inner ear, and renal dysplasia. Associated defects include asthenic habitus, long narrow facies, constricted palate, deep overbite, and myopia. Hearing loss may be due to mondini type cochlear defect and stapes fixation. Penetrance of BOR syndrome is high, although expressivity can be extremely variable. Defects in EYA1 are the cause of otofaciocervical syndrome (OFCS). The syndrome is characterized by trophic alterations of the facies and shoulder girdle in addition to the malformations seen in BOR. Defects in EYA1 are the cause of branchiootic syndrome type 1 (BOS1); also known as BO syndrome type 1 or branchiootic dysplasia. Individuals with BOS1 are affected by the same branchial and otic anomalies as those seen in individuals with BOR1, but lack renal anomalies. Defects in EYA1 are the cause of anterior segment anomalies with or without cataract (ASA). A disease characterized by various types of developmental eye anomalies, in the absence of other abnormalities. The phenotypic spectrum of anterior segment anomalies include central corneal opacity, Peters anomaly, and bilateral persistence of the pupillary membrane. Some patients have cataract. Belongs to the HAD-like hydrolase superfamily. EYA family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA repair, damage; Cell development/differentiation; EC 3.1.3.16; EC 3.1.3.48; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Protein phosphatase, tyrosine (non-receptor); Apoptosis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8q13.3 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; nucleoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity Biological Process: anatomical structure morphogenesis; double-strand break repair; histone dephosphorylation; positive regulation of DNA repair; protein sumoylation; response to ionizing radiation; sensory perception of sound Disease: Branchiootic Syndrome 1; Branchiootorenal Syndrome 1; Otofaciocervical Syndrome 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the eyes absent (EYA) family of proteins. The encoded protein may play a role in the developing kidney, branchial arches, eye, and ear. Mutations of this gene have been associated with branchiootorenal dysplasia syndrome, branchiootic syndrome, and sporadic cases of congenital cataracts and ocular anterior segment anomalies. A similar protein in mice can act as a transcriptional activator. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | Q99502 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 3183005 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2138 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q99502.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q99502,Q0P516, Q8WX80, A6NHQ0, G5E9R4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q99502 |
| Molecular Weight: | 60,660 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Eyes absent homolog 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | EYA transcriptional coactivator and phosphatase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EYA1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BOP; BOR; BOS1; OFC1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | eyes absent homolog 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Eyes absent homolog 1 |
| Protein Family: | Eyes absent |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EYA1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EYA1_HUMAN |