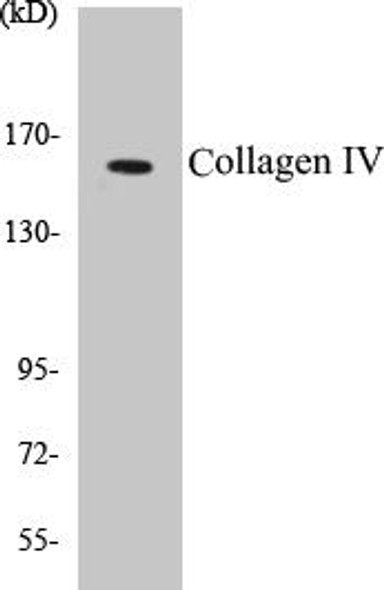
Description
| Product Name: | Collagen XI alpha1 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA |
| Product Code: | CBCAB00287 |
| ELISA Type: | Cell-Based |
| Target: | Collagen XI alpha1 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Dynamic Range: | > 5000 Cells |
| Detection Method: | Colorimetric 450 nmStorage/Stability:4°C/6 Months |
| Format: | 96-Well Microplate |
The Collagen XI alpha1 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit is a convenient, lysate-free, high throughput and sensitive assay kit that can detect Collagen XI alpha1 protein expression profile in cells. The kit can be used for measuring the relative amounts of Collagen XI alpha1 in cultured cells as well as screening for the effects that various treatments, inhibitors (ie siRNA or chemicals), or activators have on Collagen XI alpha1.
Qualitative determination of Collagen XI alpha1 concentration is achieved by an indirect ELISA format. In essence, Collagen XI alpha1 is captured by Collagen XI alpha1-specific primary antibodies while the HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies bind the Fc region of the primary antibody. Through this binding, the HRP enzyme conjugated to the secondary antibody can catalyze a colorimetric reaction upon substrate addition. Due to the qualitative nature of the Cell-Based ELISA, multiple normalization methods are needed:
| 1. | A monoclonal antibody specific for human GAPDH is included to serve as an internal positive control in normalizing the target absorbance values. |
| 2. | Following the colorimetric measurement of HRP activity via substrate addition, the Crystal Violet whole-cell staining method may be used to determine cell density. After staining, the results can be analysed by normalizing the absorbance values to cell amounts, by which the plating difference can be adjusted. |
| Database Information: | Gene ID: 1301, UniProt ID: P12107, OMIM: 120280, Unigene: Hs.523446 |
| Gene Symbol: | COL11A1 |
| Sub Type: | None |
| UniProt Protein Function: | COL11A1: May play an important role in fibrillogenesis by controlling lateral growth of collagen II fibrils. Defects in COL11A1 are the cause of Stickler syndrome type 2 (STL2); also known as Stickler syndrome vitreous type 2. STL2 is an autosomal dominant form of Stickler syndrome, an inherited disorder that associates ocular signs with more or less complete forms of Pierre Robin sequence, bone disorders and sensorineural deafness. Ocular disorders may include juvenile cataract, myopia, strabismus, vitreoretinal or chorioretinal degeneration, retinal detachment, and chronic uveitis. Robin sequence includes an opening in the roof of the mouth (a cleft palate), a large tongue (macroglossia), and a small lower jaw (micrognathia). Bones are affected by slight platyspondylisis and large, often defective epiphyses. Juvenile joint laxity is followed by early signs of arthrosis. The degree of hearing loss varies among affected individuals and may become more severe over time. Syndrome expressivity is variable. Defects in COL11A1 are the cause of Marshall syndrome (MRSHS). It is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by ocular abnormalities, deafness, craniofacial anomalies, and anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Clinical features include short stature; flat or retruded midface with short, depressed nose, flat nasal bridge and anteverted nares; cleft palate with or without the Pierre Robin sequence; appearance of large eyes with ocular hypertelorism; cataracts, either congenital or juvenile; esotropia; high myopia; sensorineural hearing loss; spondyloepiphyseal abnormalities; calcification of the falx cerebri; ectodermal abnormalities, including defects in sweating and dental structures. Defects in COL11A1 are the cause of fibrochondrogenesis type 1 (FBCG1). A severe short-limbed skeletal dysplasia characterized by broad long-bone metaphyses, pear-shaped vertebral bodies, and characteristic morphology of the growth plate, in which the chondrocytes have a fibroblastic appearance and there are regions of fibrous cartilage extracellular matrix. Clinical features include a flat midface with a small nose and anteverted nares, significant shortening of all limb segments but relatively normal hands and feet, and a small bell-shaped thorax with a protuberant abdomen. Belongs to the fibrillar collagen family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; Extracellular matrix; Secreted Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p21 Cellular Component: collagen type XI; endoplasmic reticulum lumen; extracellular region Biological Process: collagen catabolic process; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound; sensory perception of sound; visual perception Disease: Fibrochondrogenesis 1; Intervertebral Disc Disease; Marshall Syndrome; Stickler Syndrome, Type Ii |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes one of the two alpha chains of type XI collagen, a minor fibrillar collagen. Type XI collagen is a heterotrimer but the third alpha chain is a post-translationally modified alpha 1 type II chain. Mutations in this gene are associated with type II Stickler syndrome and with Marshall syndrome. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in this gene is also associated with susceptibility to lumbar disc herniation. Multiple transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P12107 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 215274245 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1301 |
| NCBI Accession: | P12107.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P12107,Q14034, Q149N0, Q9UIT4, Q9UIT5, Q9UIT6, B1ASK7 D3DT73, E9PCU0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P12107 |
| Molecular Weight: | 167,752 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Collagen alpha-1(XI) chain |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | collagen type XI alpha 1 chain |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | COL11A1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | STL2; COLL6; CO11A1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | collagen alpha-1(XI) chain |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Collagen alpha-1(XI) chain |
| Protein Family: | Collagen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | COL11A1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | COBA1_HUMAN |
| Component | Quantity |
| 96-Well Cell Culture Clear-Bottom Microplate | 2 plates |
| 10X TBS | 24 mL |
| Quenching Buffer | 24 mL |
| Blocking Buffer | 50 mL |
| 15X Wash Buffer | 50 mL |
| Primary Antibody Diluent | 12 mL |
| 100x Anti-Phospho Target Antibody | 60 µL |
| 100x Anti-Target Antibody | 60 µL |
| Anti-GAPDH Antibody | 60 µL |
| HRP-Conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Antibody | 12 mL |
| HRP-Conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody | 12 mL |
| SDS Solution | 12 mL |
| Stop Solution | 24 mL |
| Ready-to-Use Substrate | 12 mL |
| Crystal Violet Solution | 12 mL |
| Adhesive Plate Seals | 2 seals |
The following materials and/or equipment are NOT provided in this kit but are necessary to successfully conduct the experiment:
- Microplate reader able to measure absorbance at 450 nm and/or 595 nm for Crystal Violet Cell Staining (Optional)
- Micropipettes with capability of measuring volumes ranging from 1 µL to 1 ml
- 37% formaldehyde (Sigma Cat# F-8775) or formaldehyde from other sources
- Squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, multichannel pipette reservoir or automated microplate washer
- Graph paper or computer software capable of generating or displaying logarithmic functions
- Absorbent papers or vacuum aspirator
- Test tubes or microfuge tubes capable of storing ≥1 ml
- Poly-L-Lysine (Sigma Cat# P4832 for suspension cells)
- Orbital shaker (optional)
- Deionized or sterile water
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Seed 200 µL of 20,000 adherent cells in culture medium in each well of a 96-well plate. The plates included in the kit are sterile and treated for cell culture. For suspension cells and loosely attached cells, coat the plates with 100 µL of 10 µg/ml Poly-L-Lysine (not included) to each well of a 96-well plate for 30 minutes at 37°C prior to adding cells. |
| 2. | Incubate the cells for overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. |
| 3. | Treat the cells as desired. |
| 4. | Remove the cell culture medium and rinse with 200 µL of 1x TBS, twice. |
| 5. | Fix the cells by incubating with 100 µL of Fixing Solution for 20 minutes at room temperature. The 4% formaldehyde is used for adherent cells and 8% formaldehyde is used for suspension cells and loosely attached cells. |
| 6. | Remove the Fixing Solution and wash the plate 3 times with 200 µL 1x Wash Buffer for five minutes each time with gentle shaking on the orbital shaker. The plate can be stored at 4°C for a week. |
| 7. | Add 100 µL of Quenching Buffer and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. |
| 8. | Wash the plate 3 times with 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 9. | Add 200 µL of Blocking Buffer and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature. |
| 10. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 11. | Add 50 µL of 1x primary antibodies (Anti-Collagen XI alpha1 Antibody and/or Anti-GAPDH Antibody) to the corresponding wells, cover with Parafilm and incubate for 16 hours (overnight) at 4°C. If the target expression is known to be high, incubate for 2 hours at room temperature. |
| 12. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 13. | Add 50 µL of 1x secondary antibodies (HRP-Conjugated AntiRabbit IgG Antibody or HRP-Conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody) to corresponding wells and incubate for 1.5 hours at room temperature. |
| 14. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 15. | Add 50 µL of Ready-to-Use Substrate to each well and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark. |
| 16. | Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well and read OD at 450 nm immediately using the microplate reader. |
(Additional Crystal Violet staining may be performed if desired – details of this may be found in the kit technical manual.)