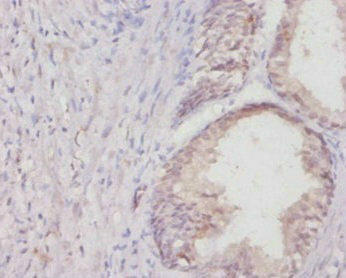
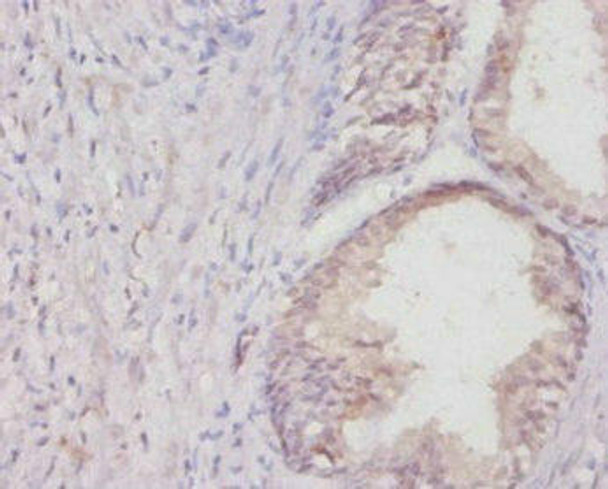
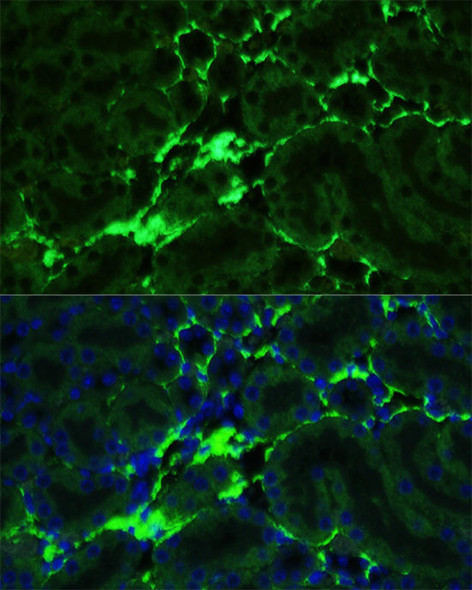
| UniProt Protein Function: | COL1A1: Type I collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen). Defects in COL1A1 are the cause of Caffey disease (CAFFD); also known as infantile cortical hyperostosis. Caffey disease is characterized by an infantile episode of massive subperiosteal new bone formation that typically involves the diaphyses of the long bones, mandible, and clavicles. The involved bones may also appear inflamed, with painful swelling and systemic fever often accompanying the illness. The bone changes usually begin before 5 months of age and resolve before 2 years of age. Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type 1 (EDS1); also known as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome gravis. EDS is a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDS1 is the severe form of classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Defects in COL1A1 are the cause of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type 7A (EDS7A); also known as autosomal dominant Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. EDS is a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDS7A is marked by bilateral congenital hip dislocation, hyperlaxity of the joints, and recurrent partial dislocations. Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 (OI1). A dominantly inherited connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility and blue sclerae. Osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 is non-deforming with normal height or mild short stature, and no dentinogenesis imperfecta. Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 2 (OI2); also known as osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. A connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility, with many perinatal fractures, severe bowing of long bones, undermineralization, and death in the perinatal period due to respiratory insufficiency. Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 3 (OI3). A connective tissue disorder characterized by progressively deforming bones, very short stature, a triangular face, severe scoliosis, grayish sclera, and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 4 (OI4); also known as osteogenesis imperfecta with normal sclerae. A connective tissue disorder characterized by moderately short stature, mild to moderate scoliosis, grayish or white sclera and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Genetic variations in COL1A1 are a cause of susceptibility to osteoporosis (OSTEOP); also known as involutional or senile osteoporosis or postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone mass, disruption of bone microarchitecture without alteration in the composition of bone. Osteoporotic bones are more at risk of fracture. A chromosomal aberration involving COL1A1 is found in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Translocation t(17;22)(q22;q13) with PDGF. Belongs to the fibrillar collagen family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Extracellular matrix; Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q26 Cellular Component: collagen; collagen type I trimer; cytoplasm; endoplasmic reticulum; extracellular matrix; extracellular region; extracellular space; Golgi apparatus; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; secretory granule Molecular Function:extracellular matrix structural constituent; identical protein binding; metal ion binding; platelet-derived growth factor binding; protease binding; protein binding Biological Process: blood vessel development; collagen biosynthetic process; collagen fibril organization; embryonic skeletal system development; endochondral ossification; extracellular matrix organization; intramembranous ossification; ossification; osteoblast differentiation; positive regulation of cell migration; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; protein transport; response to cAMP; response to corticosteroid stimulus; response to drug; response to estradiol; response to hydrogen peroxide; response to hyperoxia; response to mechanical stimulus; response to nutrient; response to nutrient levels; response to peptide hormone; response to steroid hormone; sensory perception of sound; skeletal morphogenesis; skeletal system development; skin development; skin morphogenesis; visual perception; wound healing |
| NCBI Summary: | extracellular matrix collagen protein [RGD, Feb 2006] |
| UniProt Code: | P02454 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 158711704 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 29393 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_445756.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P02454,P02455, Q63079, A3KNA1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P02454 |
| Molecular Weight: | 137,953 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | collagen alpha-1(I) chain |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | collagen type I alpha 1 chain |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Col1a1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | COLIA1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | collagen alpha-1(I) chain |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Alpha-1 type I collagen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Col1a1 |