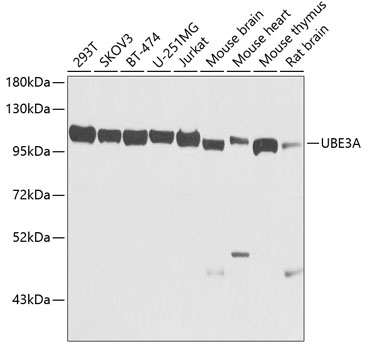
| Background: | This gene encodes an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, part of the ubiquitin protein degradation system. This imprinted gene is maternally expressed in brain and biallelically expressed in other tissues. Maternally inherited deletion of this gene causes Angelman Syndrome, characterized by severe motor and intellectual retardation, ataxia, hypotonia, epilepsy, absence of speech, and characteristic facies. The protein also interacts with the E6 protein of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, resulting in ubiquitination and proteolysis of tumor protein p53. Alternative splicing of this gene results in three transcript variants encoding three isoforms with different N-termini. Additional transcript variants have been described, but their full length nature has not been determined. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and transfers it to its substrates. Several substrates have been identified including the RAD23A and RAD23B, MCM7 (which is involved in DNA replication), annexin A1, the PML tumor suppressor, and the cell cycle regulator CDKN1B. Catalyzes the high-risk human papilloma virus E6-mediated ubiquitination of p53/TP53, contributing to the neoplastic progression of cells infected by these viruses. Additionally, may function as a cellular quality control ubiquitin ligase by helping the degradation of the cytoplasmic misfolded proteins. Finally, UBE3A also promotes its own degradation in vivo. Plays an important role in the regulation of the circadian clock: involved in the ubiquitination of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1, leading to its proteasomal degradation (PubMed:24728990). |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, part of the ubiquitin protein degradation system. This imprinted gene is maternally expressed in brain and biallelically expressed in other tissues. Maternally inherited deletion of this gene causes Angelman Syndrome, characterized by severe motor and intellectual retardation, ataxia, hypotonia, epilepsy, absence of speech, and characteristic facies. The protein also interacts with the E6 protein of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, resulting in ubiquitination and proteolysis of tumor protein p53. Alternative splicing of this gene results in three transcript variants encoding three isoforms with different N-termini. Additional transcript variants have been described, but their full length nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q05086 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 215274240 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7337 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q05086.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q05086,P78355, Q93066, Q9UEP4, Q9UEP5, Q9UEP6, Q9UEP7 Q9UEP8, Q9UEP9, A8K8Z9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q05086 |
| Molecular Weight: | 100,102 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ubiquitin protein ligase E3A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | UBE3A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AS; ANCR; E6-AP; HPVE6A; EPVE6AP |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | E6AP ubiquitin-protein ligase; HECT-type ubiquitin transferase E3A; Human papillomavirus E6-associated protein; Oncogenic protein-associated protein E6-AP; Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-54 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | UBE3A |