Cell Biology Antibodies 12
Anti-ROGDI Antibody (CAB9239)
- SKU:
- CAB9239
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ROGDI Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9239 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
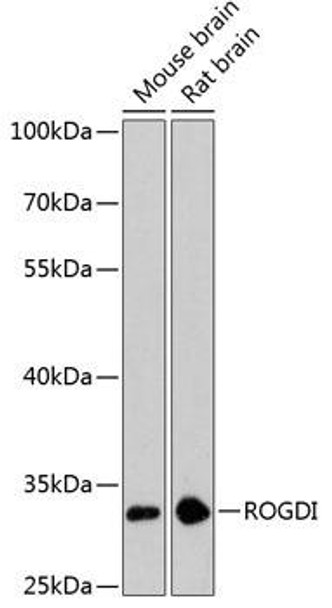
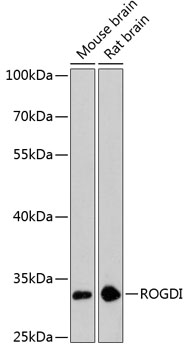
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-140 of human ROGDI (NP_078865.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-140 of human ROGDI (NP_078865.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MATV MAAT AAER AVLE EEFR WLLH DEVH AVLK QLQD ILKE ASLR FTLP GSGT EGPA KQEN FILG SCGT DQVK GVLT LQGD ALSQ ADVN LKMP RNNQ LLHF AFRE DKQW KLQQ IQDA RNHV SQAI YLLT SRDQ SYQF KTGA |
| Gene ID: | 79641 |
| Uniprot: | Q9GZN7 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus envelope |
| Calculated MW: | 32kDa |
| Observed MW: | 32kDa |
| Synonyms: | ROGDI, KTZS |
| Background: | This gene encodes a protein of unknown function. Loss-of-function mutation in this gene cause Kohlschutter-Tonz syndrome. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ROGDI: May act as a positive regulator of cell proliferation. Defects in ROGDI are the cause of Kohlschuetter-Toenz syndrome (KTZS). An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe global developmental delay, early-onset intractable seizures, spasticity, and amelogenesis imperfecta affecting both primary and secondary teeth and causing yellow or brown discoloration of the teeth. Although the phenotype is consistent, there is variability. Intellectual disability is related to the severity of seizures, and the disorder can thus be considered an epileptic encephalopathy. Some infants show normal development until seizure onset, whereas others are delayed from birth. The most severely affected individuals have profound mental retardation, never acquire speech, and become bedridden early in life. Belongs to the rogdi family.Protein type: Cell cycle regulationChromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16p13.3Cellular Component: nuclear envelope; intracellularBiological Process: positive regulation of cell proliferation; hemopoiesisDisease: Kohlschutter-tonz Syndrome |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a protein of unknown function. Loss-of-function mutation in this gene cause Kohlschutter-Tonz syndrome. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9GZN7 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 13375779 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 79641 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_078865.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9GZN7,Q6IA00 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9GZN7 |
| Molecular Weight: | 32,254 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | protein rogdi homolog |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | rogdi homolog (Drosophila) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ROGDI |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | KTZS |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein rogdi homolog; leucine zipper domain protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Protein rogdi homolog |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | |
| Protein Family: | Protein rogdi |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ROGDI |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ROGDI_HUMAN |
View AllClose