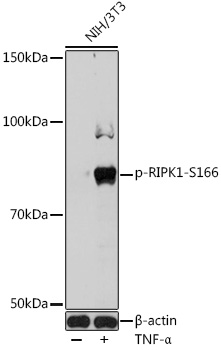
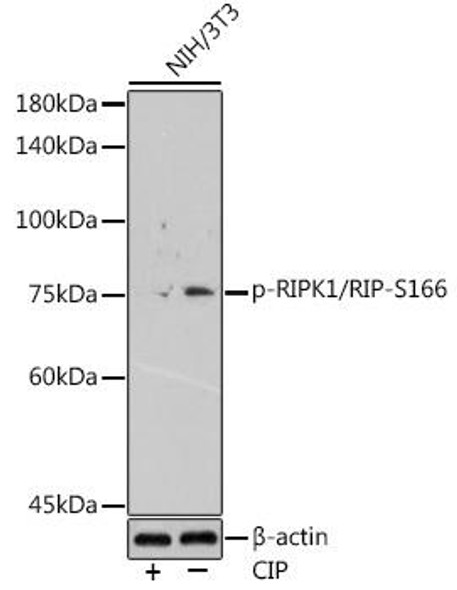
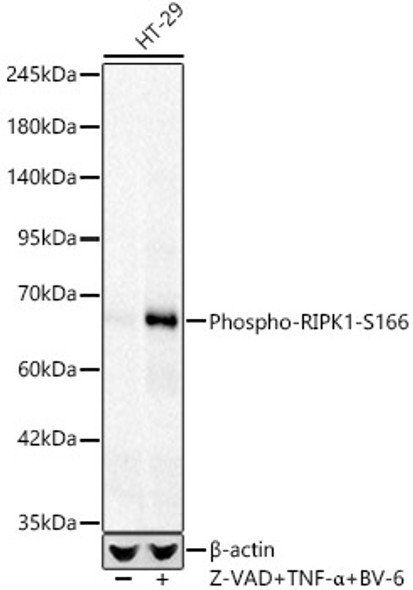
| Synonyms: | D330015H01Rik, RIP, Rinp, Rip1 |
| Background: | Serine-threonine kinase which is a key regulator of both cell death and cell survival (PubMed:25459879). Exhibits kinase activity-dependent functions that trigger cell death and kinase-independent scaffold functions regulating inflammatory signaling and cell survival (PubMed:31519887, PubMed:31519886). Initiates ripoptocide which describes cell death that is dependent on RIPK1, be it apoptosis or necroptosis (PubMed:31457011). Upon binding of TNF to TNFR1, RIPK1 is recruited to the TNF-R1 signaling complex (TNF-RSC also known as complex I) where it acts as a scaffold protein promoting cell survival, in part, by activating the canonical NF-kB pathway (PubMed:31519887, PubMed:31519886). Specific conditions can however activate RIPK1, and its kinase activity then regulates assembly of two death-inducing complexes, namely complex IIa (RIPK1-FADD-CASP8) and the complex IIb (RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL) and these complexes respectively drive apoptosis or necroptosis, a regulated form of necrosis (PubMed:29440439, PubMed:30988283, PubMed:31519887, PubMed:31519886). During embryonic development suppresses apoptosis and necroptosis and prevents the interaction of TRADD with FADD thereby limiting aberrant activation of CASP8 (PubMed:30867408, PubMed:30185824, PubMed:31511692). Phosphorylates DAB2IP at 'Ser-728' in a TNF-alpha-dependent manner, and thereby activates the MAP3K5-JNK apoptotic cascade (By similarity). Required for ZBP1-induced NF-kappaB activation and activation of NF-kappaB by DNA damage and IR (PubMed:12654725, PubMed:19590578). |
| UniProt Protein Function: | RIPK1: Serine-threonine kinase which transduces inflammatory and cell-death signals (necroptosis) following death receptors ligation, activation of pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs), and DNA damage. Upon activation of TNFR1 by the TNF-alpha family cytokines, TRADD and TRAF2 are recruited to the receptor. Ubiquitination by TRAF2 via 'Lys-63'-link chains acts as a critical enhancer of communication with downstream signal transducers in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and the NF-kappa-B pathway, which in turn mediate downstream events including the activation of genes encoding inflammatory molecules. Polyubiquitinated protein binds to IKBKG/NEMO, the regulatory subunit of the IKK complex, a critical event for NF-kappa-B activation. Interaction with other cellular RHIM-containing adapters initiates gene activation and cell death. RIPK1 and RIPK3 association, in particular, forms a necroptosis-inducing complex. Interacts (via RIP homotypic interaction motif) with RIPK3 (via RIP homotypic interaction motif); this interaction induces RIPK1 necroptosis-specific phosphorylation, formation of the necroptosis-inducing complex. Interacts (via the death domain) with TNFRSF6 (via the death domain) and TRADD (via the death domain). Is recruited by TRADD to TNFRSF1A in a TNF-dependent process. Binds RNF216, EGFR, IKBKG, TRAF1, TRAF2 and TRAF3. Interacts with BNLF1. Interacts with SQSTM1 upon TNF-alpha stimulation. May interact with MAVS/IPS1. Interacts with ZFAND5. Interacts with RBCK1. Interacts with BIRC2/c-IAP1, BIRC3/c-IAP2 and XIAP/BIRC4. Inhibited by necrostatin-1. Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, TKL; Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.11.1; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); TKL group; RIPK family Cellular Component: protein complex; mitochondrion; membrane; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; receptor complex; lipid raft Molecular Function:transferase activity; identical protein binding; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; protein binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; death receptor binding; transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups; protein complex binding; nucleotide binding; kinase activity; ATP binding; protein kinase activity Biological Process: positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; viral reproduction; positive regulation of apoptosis; protein heterooligomerization; apoptosis; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; programmed cell death; positive regulation of JNK cascade; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; positive regulation of transferase activity; signal transduction; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; protein amino acid phosphorylation; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production; positive regulation of programmed cell death; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; cellular protein catabolic process; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation; phosphorylation; positive regulation of phosphorylation; protein homooligomerization |
| UniProt Code: | Q60855 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 34328467 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 19766 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_033094.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q60855,Q3U0J3, Q8CD90, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q60855 |
| Molecular Weight: | 74,854 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | receptor (TNFRSF)-interacting serine-threonine kinase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Ripk1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | RIP; Rinp; Rip1; D330015H01Rik |
| NCBI Protein Information: | receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; RIP-1; cell death protein RIP; receptor-interacting protein 1; serine/threonine-protein kinase RIP |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cell death protein RIP; Receptor-interacting protein 1; RIP-1; Serine/threonine-protein kinase RIP |
| Protein Family: | Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Ripk1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | RIPK1_MOUSE |