Immunology Antibodies 3
Anti-Phospho-RELA-S276 Antibody (CABP0123)
- SKU:
- CABP0123
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Applications:
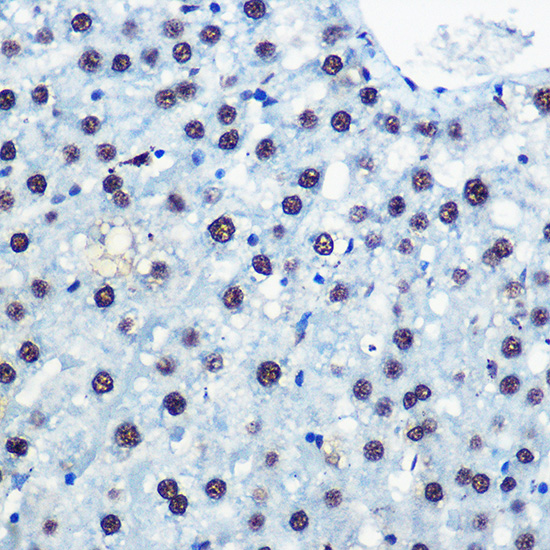
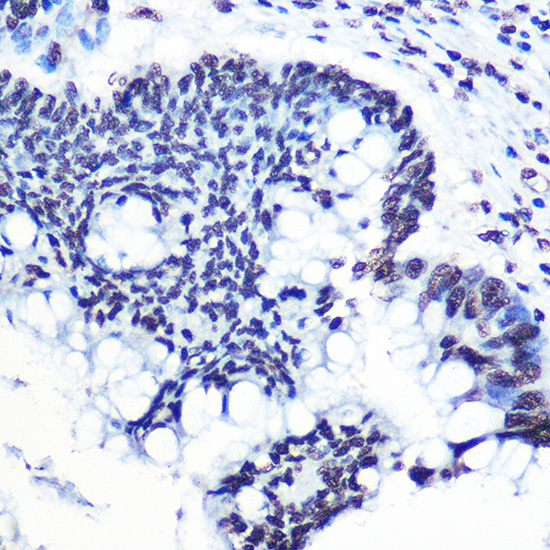
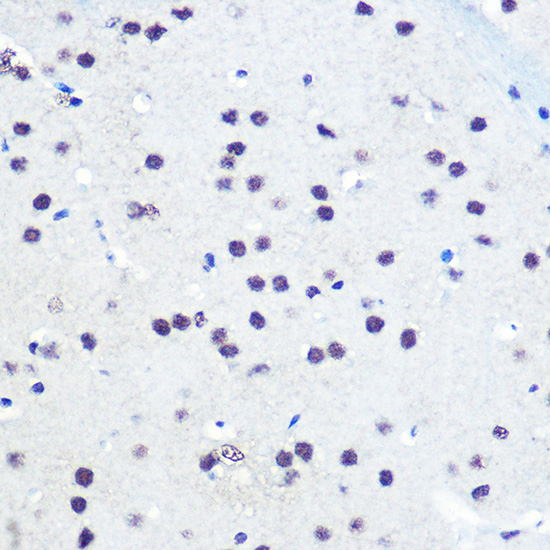
- IHC
- Applications:
- IF
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Immunology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-RELA-S276 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0123 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
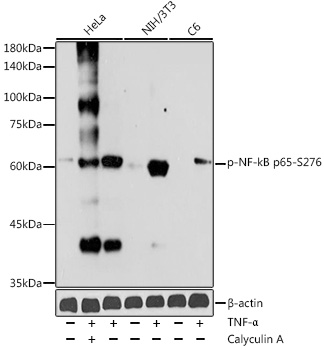
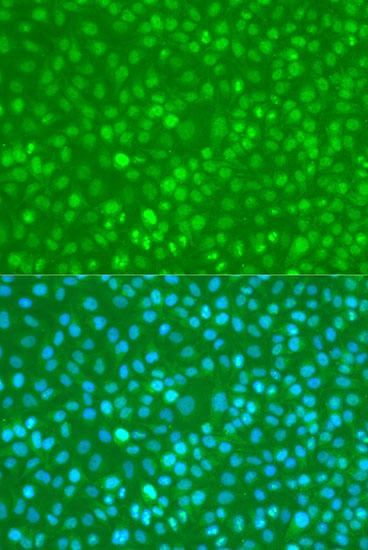
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S276 of human NF-kB p65 (NP_068810.3). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 IF 1:20 - 1:50 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, NIH/3T3, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S276 of human NF-kB p65 (NP_068810.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | RPSD R |
| Gene ID: | 5970 |
| Uniprot: | Q04206 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 58kDa/59kDa/60kDa |
| Observed MW: | 65KDa |
| Synonyms: | NFKB3, p65, NF-kB p65, RELA, CMCU |
| Background: | NF-kappa-B is a ubiquitous transcription factor involved in several biological processes. It is held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state by specific inhibitors. Upon degradation of the inhibitor, NF-kappa-B moves to the nucleus and activates transcription of specific genes. NF-kappa-B is composed of NFKB1 or NFKB2 bound to either REL, RELA, or RELB. The most abundant form of NF-kappa-B is NFKB1 complexed with the product of this gene, RELA. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NFkB-p65: a subunit of NF-kappa-B transcription complex, which plays a crucial role in inflammatory and immune responses. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B upon NF-kappa-B in the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. P65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex. There are five NFkB proteins in mammals (RelA/NFkB-p65, RelB, c-Rel, NF-_B1/NFkB-p105, and NF-_B2/NFkB-p100). They form a variety of homodimers and heterodimers, each of which activates its own characteristic set of genes. Three splice-variant isoforms have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Nuclear receptor co-regulator; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11q13.1 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol; nuclear chromatin; nucleoplasm; nucleus; transcription factor complex Molecular Function:actinin binding; chromatin binding; chromatin DNA binding; DNA binding; histone deacetylase binding; identical protein binding; NF-kappaB binding; phosphate binding; protein binding; protein heterodimerization activity; protein homodimerization activity; protein kinase binding; protein N-terminus binding; RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding; transcription activator binding; transcription factor activity; transcription factor binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding Biological Process: activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; inflammatory response; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; positive regulation of interferon type I production; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of inflammatory response; response to organic substance; response to UV-B; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway; T cell receptor signaling pathway |
| NCBI Summary: | NF-kappa-B is a ubiquitous transcription factor involved in several biological processes. It is held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state by specific inhibitors. Upon degradation of the inhibitor, NF-kappa-B moves to the nucleus and activates transcription of specific genes. NF-kappa-B is composed of NFKB1 or NFKB2 bound to either REL, RELA, or RELB. The most abundant form of NF-kappa-B is NFKB1 complexed with the product of this gene, RELA. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q04206 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 62906901 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5970 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q04206.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q04206,Q6GTV1, Q6SLK1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q04206 |
| Molecular Weight: | 59,910 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transcription factor p65 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | RELA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | p65; NFKB3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transcription factor p65 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transcription factor p65 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3 |
| Protein Family: | Proline-rich P65 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | RELA |