Cell Biology Antibodies 16
Anti-Phospho-LIM domain kinase 1-T508 Antibody (CABP0387)
- SKU:
- CABP0387
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Applications:
- IHC
- Applications:
- IF
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-LIM domain kinase 1-T508 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0387 |
| Antibody Size: | 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding T508 of human LIMK1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 IF 1:100 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
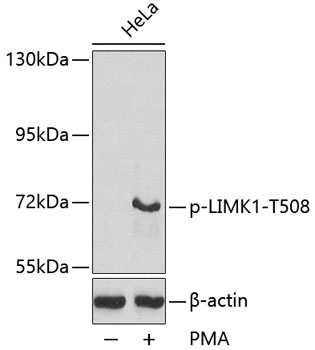
| Positive Samples: | HeLa |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding T508 of human LIMK1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 3984 |
| Uniprot: | P53667 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 33kDa/68kDa/70kDa/72kDa |
| Observed MW: | 73kDa |
| Synonyms: | LIMK1, LIMK, LIMK-1 |
| Background: | There are approximately 40 known eukaryotic LIM proteins, so named for the LIM domains they contain. LIM domains are highly conserved cysteine-rich structures containing 2 zinc fingers. Although zinc fingers usually function by binding to DNA or RNA, the LIM motif probably mediates protein-protein interactions. LIM kinase-1 and LIM kinase-2 belong to a small subfamily with a unique combination of 2 N-terminal LIM motifs and a C-terminal protein kinase domain. LIMK1 is a serine/threonine kinase that regulates actin polymerization via phosphorylation and inactivation of the actin binding factor cofilin. This protein is ubiquitously expressed during development and plays a role in many cellular processes associated with cytoskeletal structure. This protein also stimulates axon growth and may play a role in brain development. LIMK1 hemizygosity is implicated in the impaired visuospatial constructive cognition of Williams syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | LIMK1: a TKL kinase of the LISK family which mediates Rho signaling to cytoskeleton. Contains two N-terminal LIM motifs. Phosphorylated and activated by PAK1 and ROCK, downstream effectors of Rho. May be involved in brain development. Phosphorylates and inactivates the actin binding/depolymerizing factor cofilin and induces actin cytoskeletal changes. The LIM domain interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of NRG1. Binds ROCK1. Interacts with slingshot 1. Overexpressed in prostate tumors and prostate and breast cancer cell lines; manipulation of activity correlates with invasiveness in breast and prostate cancer models. Located within the 7q11.2 amplicon associated with metastatic prostate cancer. Loss of one copy of LIMK1 is the likely cause of visuospatial cognition defects seen in small chromosomal deletions associated with dominant Williams-Beuren syndrome Three splice variant have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.11.1; Protein kinase, TKL; TKL group; LISK family; LIMK subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7q11.23 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol; neuron projection; nucleoplasm Molecular Function:heat shock protein binding; protein binding; protein serine/threonine kinase activity Biological Process: actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity; nervous system development; positive regulation of actin filament bundle formation; positive regulation of axon extension; protein amino acid phosphorylation; Rho protein signal transduction; signal transduction Disease: Williams-beuren Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | There are approximately 40 known eukaryotic LIM proteins, so named for the LIM domains they contain. LIM domains are highly conserved cysteine-rich structures containing 2 zinc fingers. Although zinc fingers usually function by binding to DNA or RNA, the LIM motif probably mediates protein-protein interactions. LIM kinase-1 and LIM kinase-2 belong to a small subfamily with a unique combination of 2 N-terminal LIM motifs and a C-terminal protein kinase domain. LIMK1 is a serine/threonine kinase that regulates actin polymerization via phosphorylation and inactivation of the actin binding factor cofilin. This protein is ubiquitously expressed during development and plays a role in many cellular processes associated with cytoskeletal structure. This protein also stimulates axon growth and may play a role in brain development. LIMK1 hemizygosity is implicated in the impaired visuospatial constructive cognition of Williams syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | P53667 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 90185240 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3984 |
| NCBI Accession: | P53667.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P53667,O15283, Q15820, Q15821, Q75MU3, Q9Y5Q1, B7Z6I8 D3DXF4, D3DXF5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P53667 |
| Molecular Weight: | 68,729 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | LIM domain kinase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | LIM domain kinase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | LIMK1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LIMK; LIMK-1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | LIM domain kinase 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | LIM domain kinase 1 |
| Protein Family: | LIM domain kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | LIMK1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | LIMK1_HUMAN |