ChIP Antibodies
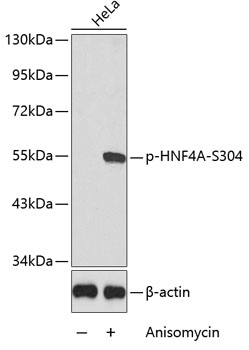
Anti-Phospho-HNF4A-S304 Antibody (CABP0362)
- SKU:
- CABP0362
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-HNF4A-S304 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0362 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
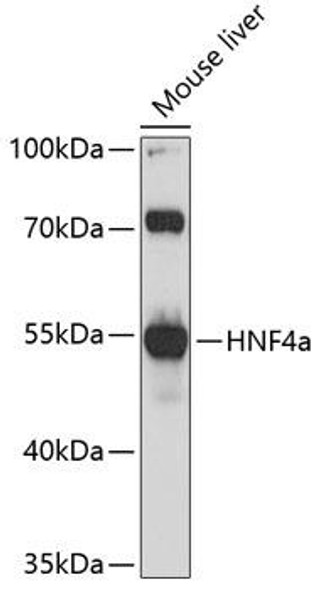
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S304 of human HNF4A |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S304 of human HNF4A |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 3172 |
| Uniprot: | P41235 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 43-56kDa |
| Observed MW: | 53kDa |
| Synonyms: | HNF4A, FRTS4, HNF4, HNF4a7, HNF4a8, HNF4a9, HNF4alpha, MODY, MODY1, NR2A1, NR2A21, TCF, TCF14 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear transcription factor which binds DNA as a homodimer. The encoded protein controls the expression of several genes, including hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha, a transcription factor which regulates the expression of several hepatic genes. This gene may play a role in development of the liver, kidney, and intestines. Mutations in this gene have been associated with monogenic autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type I. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HNF4 alpha: a nuclear transcription factor which binds DNA as a homodimer. Controls the expression of several genes, including hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha, a transcription factor which regulates the expression of several hepatic gene, alpha 1-antitrypsin, apolipoprotein CIII, and transthyretin genes. May be essential for development of the liver, kidney and intestine. Mutations have been associated with monogenic autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type I. Four alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Nuclear receptor; DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 20q13.12 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor activity; protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; DNA binding; zinc ion binding; steroid hormone receptor activity; transcription factor activity; fatty acid binding; receptor binding Biological Process: transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of lipid metabolic process; intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; lipid homeostasis; glucose homeostasis; endocrine pancreas development; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of cell proliferation; xenobiotic metabolic process; regulation of gastrulation; response to glucose stimulus; ornithine metabolic process; gene expression; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; steroid hormone mediated signaling; lipid metabolic process; negative regulation of cell growth; blood coagulation; regulation of insulin secretion; sex differentiation; phospholipid homeostasis Disease: Fanconi Renotubular Syndrome 4 With Maturity-onset Diabetes Of The Young; Maturity-onset Diabetes Of The Young, Type 1; Diabetes Mellitus, Noninsulin-dependent |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear transcription factor which binds DNA as a homodimer. The encoded protein controls the expression of several genes, including hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha, a transcription factor which regulates the expression of several hepatic genes. This gene may play a role in development of the liver, kidney, and intestines. Mutations in this gene have been associated with monogenic autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type I. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | P41235 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 148886624 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3172 |
| NCBI Accession: | P41235.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P41235,O00659, O00723, Q14540, Q5QPB8, Q6B4V5, Q6B4V6 Q6B4V7, Q92653, Q92654, A5JW41, B2RPP8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P41235 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | hepatocyte nuclear factor 4, alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HNF4A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | TCF; HNF4; MODY; FRTS4; MODY1; NR2A1; TCF14; HNF4a7; HNF4a8; HNF4a9; NR2A21; HNF4alpha |
| NCBI Protein Information: | hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha; TCF-14; HNF4alpha10/11/12; transcription factor 14; transcription factor HNF-4; hepatic nuclear factor 4 alpha; nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group A member 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group A member 1; Transcription factor 14; TCF-14; Transcription factor HNF-4 |
| Protein Family: | Hepatocyte nuclear factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HNF4A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | HNF4A_HUMAN |