Metabolism Antibodies 3
Anti-PGDH Antibody (CAB5024)
- SKU:
- CAB5024
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PGDH Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5024 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
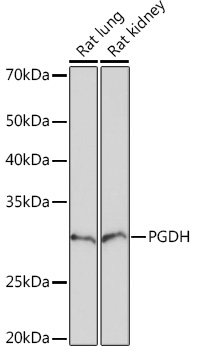
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human PGDH |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Rat lung, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human PGDH |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 3248 |
| Uniprot: | P15428 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 29kDa |
| Observed MW: | 29KDa |
| Synonyms: | 15-PGDH, PGDH, PGDH1, PHOAR1, SDR36C1 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the short-chain nonmetalloenzyme alcohol dehydrogenase protein family. The encoded enzyme is responsible for the metabolism of prostaglandins, which function in a variety of physiologic and cellular processes such as inflammation. Mutations in this gene result in primary autosomal recessive hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and cranioosteoarthropathy. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HPGD: Prostaglandin inactivation. Contributes to the regulation of events that are under the control of prostaglandin levels. Catalyzes the NAD-dependent dehydrogenation of lipoxin A4 to form 15-oxo-lipoxin A4. Inhibits in vivo proliferation of colon cancer cells. Defects in HPGD are the cause of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, primary, autosomal recessive, type 1 (PHOAR1). A disease characterized by digital clubbing, periostosis, acroosteolysis, painful joint enlargement, and variable features of pachydermia that include thickened facial skin and a thickened scalp. Other developmental anomalies include delayed closure of the cranial sutures and congenital heart disease. Defects in HPGD are the cause of cranioosteoarthropathy (COA). A form of osterarthropathy characterized by swelling of the joints, digital clubbing, hyperhidrosis, delayed closure of the fontanels, periostosis, and variable patent ductus arteriosus. Pachydermia is not a prominent feature. Defects in HPGD are a cause of isolated congenital nail clubbing (ICNC); also called clubbing of digits or hereditary acropachy. ICNC is a rare genodermatosis characterized by enlargement of the nail plate and terminal segments of the fingers and toes, resulting from proliferation of the connective tissues between the nail matrix and the distal phalanx. It is usually symmetrical and bilateral (in some cases unilateral). In nail clubbing usually the distal end of the nail matrix is relatively high compared to the proximal end, while the nail plate is complete but its dimensions and diameter more or less vary in comparison to normal. There may be different fingers and toes involved to varying degrees. Some fingers or toes are spared, but the thumbs are almost always involved. Belongs to the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Oxidoreductase; Tumor suppressor; EC 1.1.1.141 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q34-q35 Cellular Component: basolateral plasma membrane; cytosol Molecular Function:protein homodimerization activity; 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity; NAD binding; catalytic activity; prostaglandin E receptor activity Biological Process: ovulation; lipoxygenase pathway; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; cyclooxygenase pathway; arachidonic acid metabolic process; female pregnancy; parturition; negative regulation of cell cycle; prostaglandin metabolic process Disease: Digital Clubbing, Isolated Congenital; Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy, Primary, Autosomal Recessive, 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the short-chain nonmetalloenzyme alcohol dehydrogenase protein family. The encoded enzyme is responsible for the metabolism of prostaglandins, which function in a variety of physiologic and cellular processes such as inflammation. Mutations in this gene result in primary autosomal recessive hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and cranioosteoarthropathy. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P15428 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 129889 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3248 |
| NCBI Accession: | P15428.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P15428,O00749, Q06F08, Q12998, B4DTA4, B4DU74, B4DV57 D3DP43, E7EV11, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P15428 |
| Molecular Weight: | 29kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase 15-(NAD) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HPGD |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PGDH; PGDH1; PHOAR1; 15-PGDH; SDR36C1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [NAD(+)]; 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [NAD(+)]; prostaglandin dehydrogenase 1; NAD+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase; short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 36C, member 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [NAD(+)] |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Prostaglandin dehydrogenase 1 |
| Protein Family: | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HPGD |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PGDH_HUMAN |
View AllClose