Cell Biology Antibodies 17
Anti-NQO1 Antibody (CAB19586)
- SKU:
- CAB19586
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-NQO1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19586 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human NQO1. |
| Application: | WB IHC IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
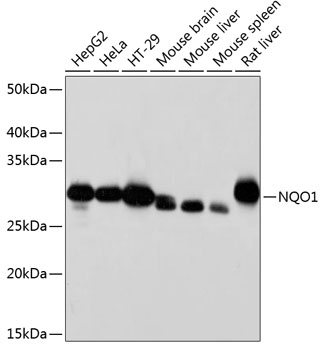
| Positive Samples: | HepG2, HeLa, HT-29, Mouse brain, Mouse liver, Mouse spleen, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human NQO1. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1728 |
| Uniprot: | P15559 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 31kDa |
| Observed MW: | 31KDa |
| Synonyms: | DHQU, DIA4, DTD, NMOR1, NMORI, QR1, NQO1 |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. This FAD-binding protein forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. This protein's enzymatic activity prevents the one electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in this gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of this protein has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NQO1: a FAD-binding flavoprotein enzyme that that prevents the one electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Involved in detoxification pathways as well as in biosynthetic processes such as the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation of glutamate residues in prothrombin synthesis. Mutations have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. The expression of NQO1 is increased in liver, colon and breast tumors and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) compared with the normal tissues. Moreover, expression levels are also elevated in developing tumors, suggesting a role for NQ01 in the prevention of tumor development. A homozygous common missense variant (NQO1(*)2, rs1800566(T)), that disables NQO1 strongly predicts poor survival among two independent series of women with breast cancer. Studies on NQO1 knockout mice suggest that the lack of NQO1 enzymatic activity changes intracellular redox states resulting in a reduction in apoptosis, which in turn leads to myeloid hyperplasia of bone marrow. Altered expression is associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Inhibited by dicoumarol. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Oxidoreductase; EC 1.6.5.2 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16q22.1 Cellular Component: cell soma; cytoplasm; cytosol Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) activity; cytochrome-b5 reductase activity; superoxide dismutase activity Biological Process: response to ethanol; removal of superoxide radicals; response to toxin; xenobiotic metabolic process; positive regulation of neuron apoptosis; negative regulation of catalytic activity; regulation of amino acid metabolic process; nitric oxide biosynthetic process; response to nutrient; response to estradiol stimulus; aging; synaptic transmission, cholinergic |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. This FAD-binding protein forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. This protein's enzymatic activity prevents the one electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in this gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of this protein has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P15559 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 118607 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1728 |
| NCBI Accession: | P15559.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P15559 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | NQO1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DTD; QR1; DHQU; DIA4; NMOR1; NMORI |
| NCBI Protein Information: | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Azoreductase; DT-diaphorase; DTD; Menadione reductase; NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1; Phylloquinone reductase; Quinone reductase 1; QR1 |
| Protein Family: | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | NQO1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NQO1_HUMAN |