Cell Biology Antibodies 12
Anti-HAS2 Antibody (CAB9897)
- SKU:
- CAB9897
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-HAS2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9897 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
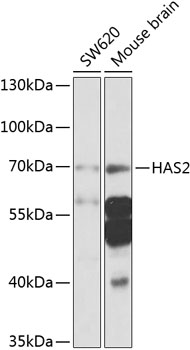
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 67-185 of human HAS2 (NP_005319.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | SW620, Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 67-185 of human HAS2 (NP_005319.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | EHRK MKKS LETP IKLN KTVA LCIA AYQE DPDY LRKC LQSV KRLT YPGI KVVM VIDG NSED DLYM MDIF SEVM GRDK SATY IWKN NFHE KGPG ETDE SHKE SSQH VTQL VLSN KSIC IMQ |
| Gene ID: | 3037 |
| Uniprot: | Q92819 |
| Cellular Location: | Membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 63kDa |
| Observed MW: | 70kDa |
| Synonyms: | HAS2 |
| Background: | Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, the interaction of HA with the leukocyte receptor CD44 is important in tissue-specific homing by leukocytes, and overexpression of HA receptors has been correlated with tumor metastasis. HAS2 is a member of the newly identified vertebrate gene family encoding putative hyaluronan synthases, and its amino acid sequence shows significant homology to glycosaminoglycan synthetase (DG42) from Xenopus laevis, and human and murine hyaluronan synthase 1. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HAS2: Plays a role in hyaluronan/hyaluronic acid (HA) synthesis. Expressed in fibroblasts. Belongs to the nodC/HAS family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Transferase; EC 2.4.1.212; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8q24.12 Cellular Component: integral to plasma membrane Molecular Function:hyaluronan synthase activity Biological Process: extracellular polysaccharide biosynthetic process; hyaluronan biosynthetic process; positive regulation of cell proliferation; kidney development; vasculogenesis; positive regulation of cell migration |
| NCBI Summary: | Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, the interaction of HA with the leukocyte receptor CD44 is important in tissue-specific homing by leukocytes, and overexpression of HA receptors has been correlated with tumor metastasis. HAS2 is a member of the newly identified vertebrate gene family encoding putative hyaluronan synthases, and its amino acid sequence shows significant homology to glycosaminoglycan synthetase (DG42) from Xenopus laevis, and human and murine hyaluronan synthase 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q92819 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 4885391 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3037 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_005319.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q92819,Q32MM3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q92819 |
| Molecular Weight: | 63566 |
| NCBI Full Name: | hyaluronan synthase 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | hyaluronan synthase 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HAS2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | hyaluronan synthase 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Hyaluronan synthase 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Hyaluronate synthase 2; Hyaluronic acid synthase 2; HA synthase 2 |
| Protein Family: | Hyaluronan synthase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HAS2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | HYAS2_HUMAN |
View AllClose