Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CLEC4M Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB14268 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 280-399 of human CLEC4M (NP_055072.3). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
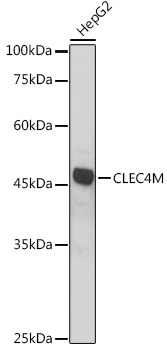
| Positive Samples: | HepG2 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 280-399 of human CLEC4M (NP_055072.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | YFMS NSQR NWHD SVTA CQEV RAQL VVIK TAEE QNFL QLQT SRSN RFSW MGLS DLNQ EGTW QWVD GSPL SPSF QRYW NSGE PNNS GNED CAEF SGSG WNDN RCDV DNYW ICKK PAAC FRDE |
| Gene ID: | 10332 |
| Uniprot: | Q9H2X3 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Secreted, Single-pass type II membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 24-45kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45KDa |
| Synonyms: | CLEC4M, CD209L, CD299, DC-SIGN2, DC-SIGNR, DCSIGNR, HP10347, L-SIGN, LSIGN |
| Background: | This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as L-SIGN because of its expression in the endothelial cells of the lymph nodes and liver. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses, with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are common and have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 30835; often referred to as DC-SIGN or CD209). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Probable pathogen-recognition receptor involved in peripheral immune surveillance in liver. May mediate the endocytosis of pathogens which are subsequently degraded in lysosomal compartments. Is a receptor for ICAM3, probably by binding to mannose-like carbohydrates. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as L-SIGN because of its expression in the endothelial cells of the lymph nodes and liver. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses, with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are common and have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 30835; often referred to as DC-SIGN or CD209). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9H2X3 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 223278337 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 10332 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_001138377.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9H2X3,Q69F40, Q969M4, Q96QP3, Q96QP4, Q96QP5, Q96QP6 Q9BXS3, Q9H2Q9, Q9H8F0, A6NKI4, A8K8B3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9H2X3 |
| Molecular Weight: | 60 |
| NCBI Full Name: | C-type lectin domain family 4 member M isoform 12 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | C-type lectin domain family 4 member M |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CLEC4M |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CD299; LSIGN; CD209L; L-SIGN; DCSIGNR; HP10347; DC-SIGN2; DC-SIGNR |
| NCBI Protein Information: | C-type lectin domain family 4 member M |
| UniProt Protein Name: | C-type lectin domain family 4 member M |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | CD209 antigen-like protein 1; DC-SIGN-related protein; DC-SIGNR; Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 2; DC-SIGN2; Liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin; L-SIGN; CD_antigen: CD299 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CLEC4M |