Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-Claudin-16 Antibody (CAB9862)
- SKU:
- CAB9862
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Claudin-16 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9862 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 50-150 of human CLDN16 (NP_006571.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
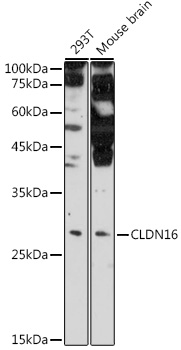
| Positive Samples: | 293T, Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 50-150 of human CLDN16 (NP_006571.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | HLSG ARAG VCPC CHPD GLLA TMRD LLQY IACF FAFF SAGF LIVA TWTD CWMV NADD SLEV STKC RGLW WECV TNAF DGIR TCDE YDSI LAEH PLKL VVTR A |
| Gene ID: | 10686 |
| Uniprot: | Q9Y5I7 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein, tight junction |
| Calculated MW: | 33kDa |
| Observed MW: | 30kDa |
| Synonyms: | CLDN16, HOMG3, PCLN1 |
| Background: | Tight junctions represent one mode of cell-to-cell adhesion in epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, forming continuous seals around cells and serving as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space. These junctions are comprised of sets of continuous networking strands in the outwardly facing cytoplasmic leaflet, with complementary grooves in the inwardly facing extracytoplasmic leaflet. The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the claudin family, is an integral membrane protein and a component of tight junction strands. It is found primarily in the kidneys, specifically in the thick ascending limb of Henle, where it acts as either an intercellular pore or ion concentration sensor to regulate the paracellular resorption of magnesium ions. Defects in this gene are a cause of primary hypomagnesemia, which is characterized by massive renal magnesium wasting with hypomagnesemia and hypercalciuria, resulting in nephrocalcinosis and renal failure. This gene and the CLDN1 gene are clustered on chromosome 3q28. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Claudin-16: Plays a major role in tight junction-specific obliteration of the intercellular space, through calcium- independent cell-adhesion activity. Involved in paracellular magnesium reabsorption. Required for a selective paracellular conductance. May form, alone or in partnership with other constituents, an intercellular pore permitting paracellular passage of magnesium and calcium ions down their electrochemical gradients. Alternatively, it could be a sensor of magnesium concentration that could alter paracellular permeability mediated by other factors. Defects in CLDN16 are the cause of hypomagnesemia type 3 (HOMG3); also known as familial hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis (FHHNC). HOMG3 is a progressive renal disease characterized by primary renal magnesium wasting with hypomagnesemia, hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis. Recurrent urinary tract infections and kidney stones are often observed. In spite of hypercalciuria, patients do not show hypocalcemia. Belongs to the claudin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell adhesion; Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3q28 Cellular Component: tight junction Molecular Function:identical protein binding; magnesium ion transmembrane transporter activity; protein binding Biological Process: calcium-independent cell-cell adhesion; cellular metal ion homeostasis; excretion Disease: Hypomagnesemia 3, Renal |
| NCBI Summary: | Tight junctions represent one mode of cell-to-cell adhesion in epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, forming continuous seals around cells and serving as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space. These junctions are comprised of sets of continuous networking strands in the outwardly facing cytoplasmic leaflet, with complementary grooves in the inwardly facing extracytoplasmic leaflet. The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the claudin family, is an integral membrane protein and a component of tight junction strands. It is found primarily in the kidneys, specifically in the thick ascending limb of Henle, where it acts as either an intercellular pore or ion concentration sensor to regulate the paracellular resorption of magnesium ions. Defects in this gene are a cause of primary hypomagnesemia, which is characterized by massive renal magnesium wasting with hypomagnesemia and hypercalciuria, resulting in nephrocalcinosis and renal failure. This gene and the CLDN1 gene are clustered on chromosome 3q28. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9Y5I7 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6685318 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 10686 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9Y5I7.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9Y5I7 |
| Molecular Weight: | 34kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Claudin-16 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | claudin 16 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CLDN16 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HOMG3; PCLN1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | claudin-16 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Claudin-16 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Paracellin-1; PCLN-1 |
| Protein Family: | Claudin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CLDN16 |
View AllClose