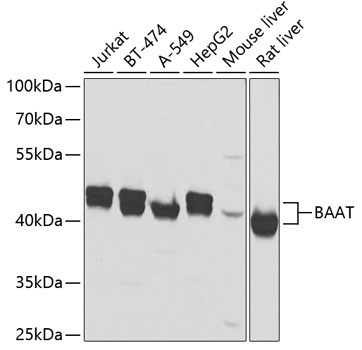
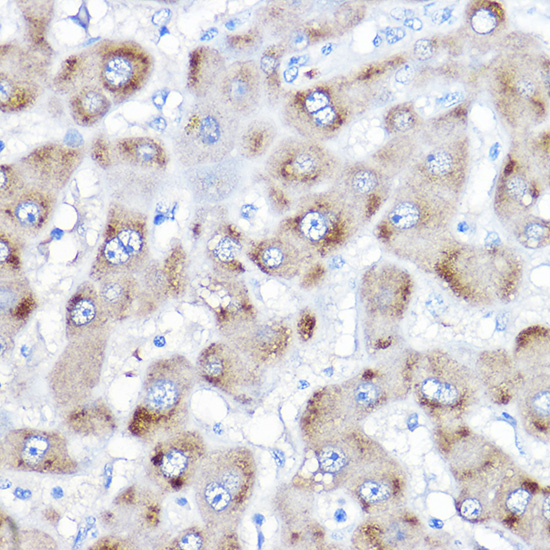
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-BAAT Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7646 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 309-418 of human BAAT (NP_001692.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Jurkat, BT-474, A-549, HepG2, Mouse liver, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 309-418 of human BAAT (NP_001692.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | YLFP IEEA QGQF LFIV GEGD KTIN SKAH AEQA IGQL KRHG KNNW TLLS YPGA GHLI EPPY SPLC CAST THDL RLHW GGEV IPHA AAQE HAWK EIQR FLRK HLIP DVTS QL |
| Gene ID: | 570 |
| Uniprot: | Q14032 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 46kDa |
| Observed MW: | 40-46kDa |
| Synonyms: | BAAT, BACAT, BAT |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of C24 bile acids from the acyl-CoA thioester to either glycine or taurine, the second step in the formation of bile acid-amino acid conjugates. The bile acid conjugates then act as a detergent in the gastrointestinal tract, which enhances lipid and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial hypercholanemia (FHCA). Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | BAAT: Involved in bile acid metabolism. In liver hepatocytes catalyzes the second step in the conjugation of C24 bile acids (choloneates) to glycine and taurine before excretion into bile canaliculi. The major components of bile are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. In a first step the bile acids are converted to an acyl-CoA thioester, either in peroxisomes (primary bile acids deriving from the cholesterol pathway), or cytoplasmic at the endoplasmic reticulum (secondary bile acids). May catalyze the conjugation of primary or secondary bile acids, or both. The conjugation increases the detergent properties of bile acids in the intestine, which facilitates lipid and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. In turn, bile acids are deconjugated by bacteria in the intestine and are recycled back to the liver for reconjugation (secondary bile acids). May also act as an acyl-CoA thioesterase that regulates intracellular levels of free fatty acids. In vitro, catalyzes the hydrolysis of long- and very long-chain saturated acyl-CoAs to the free fatty acid and coenzyme A (CoASH), and conjugates glycine to these acyl-CoAs. Defects in BAAT are involved in familial hypercholanemia (FHCA). FHCA is a disorder characterized by elevated serum bile acid concentrations, itching, and fat malabsorption. Belongs to the C/M/P thioester hydrolase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Hydrolase; Other Amino Acids Metabolism - taurine and hypotaurine; Lipid Metabolism - unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis; Lipid Metabolism - primary bile acid biosynthesis; EC 2.3.1.65; Transferase; EC 3.1.2.2 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9q22.3 Cellular Component: cytosol; peroxisomal matrix; peroxisome Molecular Function:glycine N-choloyltransferase activity; N-acyltransferase activity; protein binding; receptor binding; transferase activity, transferring acyl groups Biological Process: acyl-CoA metabolic process; bile acid biosynthetic process; bile acid metabolic process; glycine metabolic process; taurine metabolic process Disease: Hypercholanemia, Familial |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of C24 bile acids from the acyl-CoA thioester to either glycine or taurine, the second step in the formation of bile acid-amino acid conjugates. The bile acid conjugates then act as a detergent in the gastrointestinal tract, which enhances lipid and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial hypercholanemia (FHCA). Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q14032 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 74739811 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 570 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q14032.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q14032,Q3B7W9, Q96L31, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q14032 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,299 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | BAAT |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BAT; BACAT |
| NCBI Protein Information: | bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glycine N-choloyltransferase; Long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA hydrolase |
| Protein Family: | Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | BAAT |
| UniProt Entry Name: | BAAT_HUMAN |