Cell Biology Antibodies 7
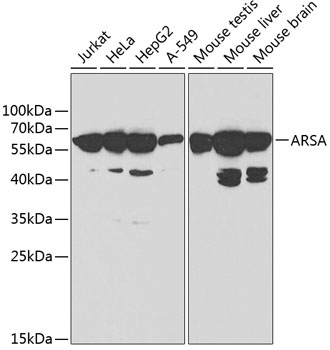
Anti-ARSA Antibody (CAB1736)
- SKU:
- CAB1736
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ARSA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1736 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 210-509 of human ARSA (NP_000478.3). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | Jurkat, HeLa, HepG2, A-549, Mouse testis, Mouse liver, Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 210-509 of human ARSA (NP_000478.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LMAD AQRQ DRPF FLYY ASHH THYP QFSG QSFA ERSG RGPF GDSL MELD AAVG TLMT AIGD LGLL EETL VIFT ADNG PETM RMSR GGCS GLLR CGKG TTYE GGVR EPAL AFWP GHIA PGVT HELA SSLD LLPT LAAL AGAP LPNV TLDG FDLS PLLL GTGK SPRQ SLFF YPSY PDEV RGVF AVRT GKYK AHFF TQGS AHSD TTAD PACH ASSS LTAH EPPL LYDL SKDP GENY NLLG GVAG ATPE VLQA LKQL QLLK AQLD AAVT FGPS QVAR GEDP ALQI CCHP GCTP RPAC CHCP DPHA |
| Gene ID: | 410 |
| Uniprot: | P15289 |
| Cellular Location: | Lysosome |
| Calculated MW: | 44kDa/53kDa |
| Observed MW: | 66kDa |
| Synonyms: | ARSA, MLD |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate to cerebroside and sulfate. Defects in this gene lead to metachromatic leucodystrophy (MLD), a progressive demyelination disease which results in a variety of neurological symptoms and ultimately death. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ARSA: Hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate. Defects in ARSA are a cause of leukodystrophy metachromatic (MLD). MLD is a disease due to a lysosomal storage defect. It is characterized by intralysosomal storage of cerebroside-3-sulfate in neural and non-neural tissues, with a diffuse loss of myelin in the central nervous system. Progressive demyelination causes a variety of neurological symptoms, including gait disturbances, ataxias, optical atrophy, dementia, seizures, and spastic tetraparesis. Three forms of the disease can be distinguished according to the age at onset: late- infantile, juvenile and adult. Arylsulfatase A activity is defective in multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD). A clinically and biochemically heterogeneous disorder caused by the simultaneous impairment of all sulfatases, due to defective post-translational modification and activation. It combines features of individual sulfatase deficiencies such as metachromatic leukodystrophy, mucopolysaccharidosis, chondrodysplasia punctata, hydrocephalus, ichthyosis, neurologic deterioration and developmental delay. Arylsulfatase A activity is impaired in multiple sulfatase deficiency due to mutations in SUMF1. SUMF1 mutations result in defective post-translational modification of ARSA at residue Cys- 69 that is not converted to 3-oxoalanine. Belongs to the sulfatase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Hydrolase; Lipid Metabolism - sphingolipid; EC 3.1.6.8 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q13.33 Cellular Component: extracellular space; lysosomal lumen; extrinsic to external side of plasma membrane; lysosome; endoplasmic reticulum lumen; acrosome; integral to membrane; endosome Molecular Function:arylsulfatase activity; sulfuric ester hydrolase activity; calcium ion binding; cerebroside-sulfatase activity Biological Process: sphingolipid metabolic process; response to ethanol; central nervous system development; cellular protein metabolic process; binding of sperm to zona pellucida; response to estrogen stimulus; response to methylmercury; autophagy; glycosphingolipid metabolic process; post-translational protein modification; response to nutrient; response to pH Disease: Metachromatic Leukodystrophy |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate to cerebroside and sulfate. Defects in this gene lead to metachromatic leucodystrophy (MLD), a progressive demyelination disease which results in a variety of neurological symptoms and ultimately death. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P15289 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 114221 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 410 |
| NCBI Accession: | P15289.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P15289,Q6ICI5, Q96CJ0, B2RCA6, B7XD04, F8WCC8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P15289 |
| Molecular Weight: | 507 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Arylsulfatase A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | arylsulfatase A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ARSA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MLD |
| NCBI Protein Information: | arylsulfatase A; ASA; cerebroside-sulfatase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Arylsulfatase A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cerebroside-sulfataseCleaved into the following 2 chains:Arylsulfatase A component B; Arylsulfatase A component C |
| Protein Family: | Arylsulfatase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ARSA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ARSA_HUMAN |