Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ACSL4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB6826 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
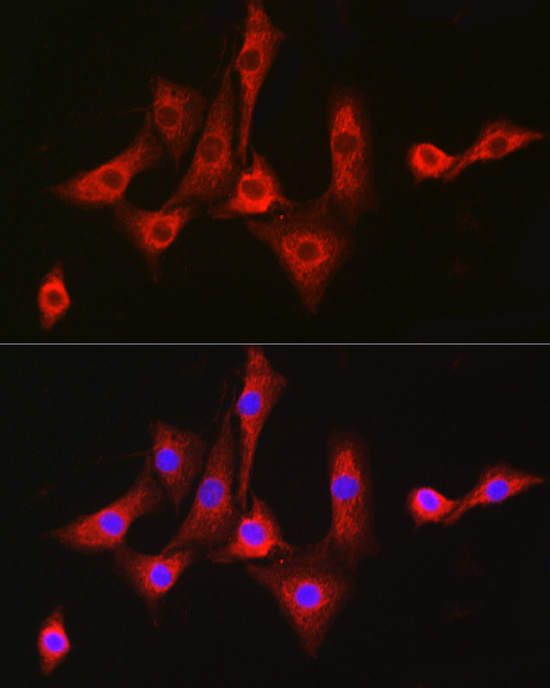
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-280 of human ACSL4 (NP_004449.1). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
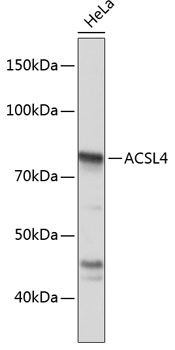
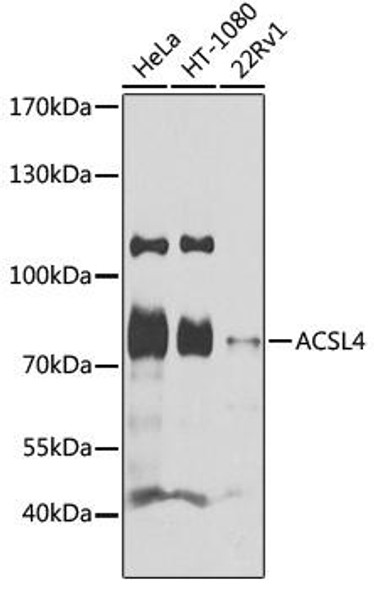
| Positive Samples: | HeLa |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-280 of human ACSL4 (NP_004449.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MAKR IKAK PTSD KPGS PYRS VTHF DSLA VIDI PGAD TLDK LFDH AVSK FGKK DSLG TREI LSEE NEMQ PNGK VFKK LILG NYKW MNYL EVNR RVNN FGSG LTAL GLKP KNTI AIFC ETRA EWMI AAQT CFKY NFPL VTLY ATLG KEAV VHGL NESE ASYL ITSV ELLE SKLK TALL DISC VKHI IYVD NKAI NKAE YPEG FEIH SMQS VEEL GSNP ENLG IPPS RPTP SDMA IVMY TSGS TGRP KGVM MHHS NLIA GMTG QCER IPGL GPKD TYIG YLPL |
| Gene ID: | 2182 |
| Uniprot: | O60488 |
| Cellular Location: | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Microsome membrane, Mitochondrion outer membrane, Peroxisome membrane, Single-pass type III membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 74kDa/79kDa |
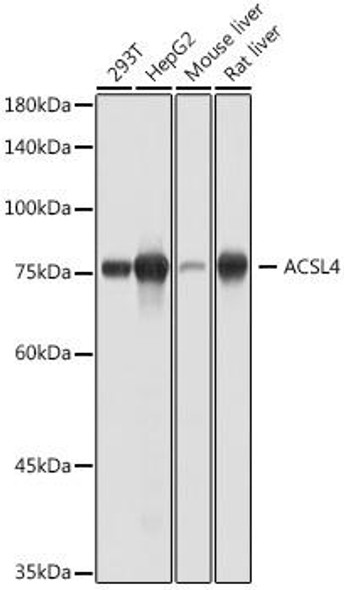
| Observed MW: | 80KDa |
| Synonyms: | ACSL4, ACS4, FACL4, LACS4, MRX63, MRX68 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of the long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme preferentially utilizes arachidonate as substrate. The absence of this enzyme may contribute to the mental retardation or Alport syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene generates multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ACSL4: Activation of long-chain fatty acids for both synthesis of cellular lipids, and degradation via beta-oxidation. Preferentially uses arachidonate and eicosapentaenoate as substrates. Defects in ACSL4 are the cause of mental retardation X- linked type 63 (MRX63). Mental retardation is a mental disorder characterized by significantly sub-average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptative behavior and manifested during the developmental period. Non- syndromic mental retardation patients do not manifest other clinical signs. Defects in ACSL4 are involved in Alport syndrome with mental retardation midface hypoplasia and elliptocytosis (ATS-MR). A X-linked contiguous gene deletion syndrome characterized by glomerulonephritis, deafness, mental retardation, midface hypoplasia and elliptocytosis. Belongs to the ATP-dependent AMP-binding enzyme family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid Metabolism - fatty acid; Membrane protein, integral; EC 6.2.1.3; Ligase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq22.3-q23 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; lipid particle; membrane Molecular Function:arachidonate-CoA ligase activity; long-chain-fatty-acid-CoA ligase activity; very-long-chain-fatty-acid-CoA ligase activity Biological Process: lipid metabolic process Disease: Mental Retardation, X-linked 63 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of the long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme preferentially utilizes arachidonate as substrate. The absence of this enzyme may contribute to the mental retardation or Alport syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene generates multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016] |
| UniProt Code: | O60488 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 13432172 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2182 |
| NCBI Accession: | O60488.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O60488,O60848, O60849, Q5JWV8, D3DUY2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O60488 |
| Molecular Weight: | 74,436 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ACSL4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ACS4; FACL4; LACS4; MRX63; MRX68 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4; LACS 4 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ACSL4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ACSL4_HUMAN |